
在金融领域,为了保证数据的精度,往往会使用BigDecimal。本文就来探讨下为什么BigDecimal可以保证精度不丢失。
类介绍
首先来看一下BigDecimal的类声明以及几个属性:
public classBigDecimalextendsNumberimplementsComparable<BigDecimal> {
// 该BigDecimal的未缩放值
privatefinal BigInteger intVal;
// 精度,可以理解成小数点后的位数
privatefinalint scale;
// BigDecimal中的十进制位数,如果位数未知,则为0(备用信息)
privatetransientint precision;
// Used to store the canonical string representation, if computed.
// 这个我理解就是存实际的BigDecimal值
privatetransient String stringCache;
// 扩大成long型数值后的值
privatefinaltransientlong intCompact;
}
从例子入手
通过debug来发现源码中的奥秘是了解类运行机制很好的方式。请看下面的testBigDecimal方法:
@Test
publicvoidtestBigDecimal(){
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(2.36);
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3.5);
BigDecimal resDecimal = bigDecimal1.add(bigDecimal2);
System.out.println(resDecimal);
}
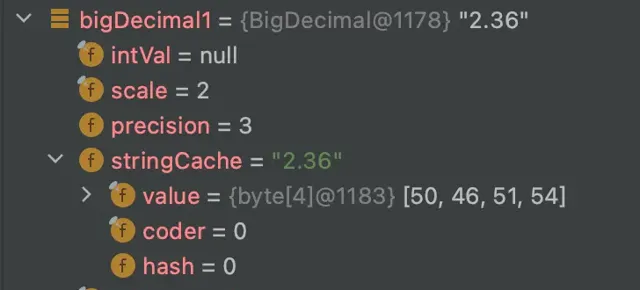
在执行了
BigDecimal.valueOf(2.36)
后,查看debug信息可以发现上述提到的几个属性被赋了值:
接下来进到add方法里面,看看它是怎么计算的:
/**
* Returns a BigDecimal whose value is (this + augend),
* and whose scale is max(this.scale(), augend.scale()).
*/
public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend){
if (this.intCompact != INFLATED) {
if ((augend.intCompact != INFLATED)) {
return add(this.intCompact, this.scale, augend.intCompact, augend.scale);
} else {
return add(this.intCompact, this.scale, augend.intVal, augend.scale);
}
} else {
if ((augend.intCompact != INFLATED)) {
return add(augend.intCompact, augend.scale, this.intVal, this.scale);
} else {
return add(this.intVal, this.scale, augend.intVal, augend.scale);
}
}
}
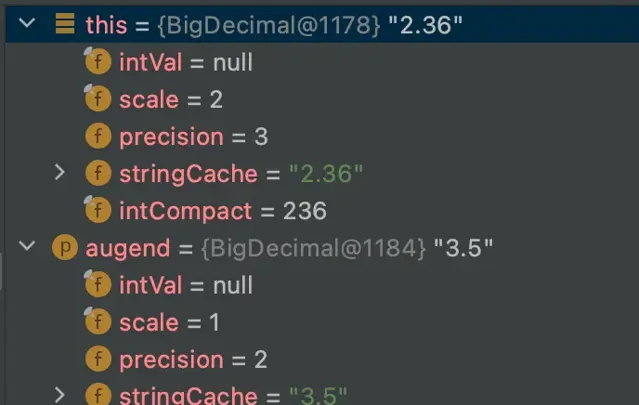
看一下传进来的值:
进入第8行的add方法:
privatestatic BigDecimal add(finallong xs, int scale1, finallong ys, int scale2){
long sdiff = (long) scale1 - scale2;
if (sdiff == 0) {
return add(xs, ys, scale1);
} elseif (sdiff < 0) {
int raise = checkScale(xs,-sdiff);
long scaledX = longMultiplyPowerTen(xs, raise);
if (scaledX != INFLATED) {
return add(scaledX, ys, scale2);
} else {
BigInteger bigsum = bigMultiplyPowerTen(xs,raise).add(ys);
return ((xs^ys)>=0) ? // same sign test
new BigDecimal(bigsum, INFLATED, scale2, 0)
: valueOf(bigsum, scale2, 0);
}
} else {
int raise = checkScale(ys,sdiff);
long scaledY = longMultiplyPowerTen(ys, raise);
if (scaledY != INFLATED) {
return add(xs, scaledY, scale1);
} else {
BigInteger bigsum = bigMultiplyPowerTen(ys,raise).add(xs);
return ((xs^ys)>=0) ?
new BigDecimal(bigsum, INFLATED, scale1, 0)
: valueOf(bigsum, scale1, 0);
}
}
}
这个例子中,该方法传入的参数分别是:xs=236,scale1=2,ys=35,scale2=1
该方法首先计算scale1 - scale2,根据差值走不同的计算逻辑,这里求出来是1,所以进入到最下面的else代码块(这块是关键):
首先17行校验了一下数值范围
18行将ys扩大了10的n次倍,这里n=raise=1,所以返回的scaledY=350
接着就进入到20行的add方法:
privatestatic BigDecimal add(long xs, long ys, int scale){
long sum = add(xs, ys);
if (sum!=INFLATED)
return BigDecimal.valueOf(sum, scale);
returnnew BigDecimal(BigInteger.valueOf(xs).add(ys), scale);
}
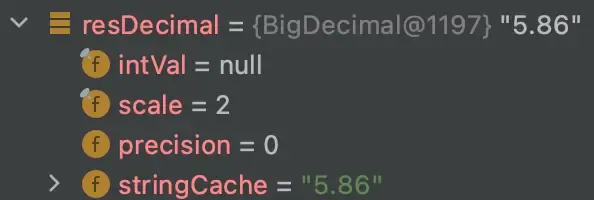
这个方法很简单,就是计算和,然后返回BigDecimal对象:
结论
所以可以得出结论:BigDecimal在计算时,实际会把数值扩大10的n次倍,变成一个long型整数进行计算,整数计算时自然可以实现精度不丢失。同时结合精度scale,实现最终结果的计算。
来源:juejin.cn/post/7348709938023940136
>>
END
精品资料,超赞福利,免费领
微信扫码/长按识别 添加【技术交流群】
群内每天分享精品学习资料

最近开发整理了一个用于速刷面试题的小程序;其中收录了上千道常见面试题及答案(包含基础、并发、JVM、MySQL、Redis、Spring、SpringMVC、SpringBoot、SpringCloud、消息队列等多个类型),欢迎您的使用。
👇👇
👇点击"阅读原文",获取更多资料(持续更新中)











