为什么要在编写组件之前就要做好日志规范的设计和定义呢?那我还是来一段GPT为我们解答的内容和日志规范设计的一些基础。 设计一个良好的程序日志规范对C#项目的维护和调试非常重要。 以下是一个C#程序日志规范的建议,包括日志的级别、格式、内容和使用注意事项。
一、日志级别
Trace :最详细的信息,通常只在开发期间启用,用于记录程序的所有细节。
Debug :调试信息,开发和测试期间使用,记录较为详细的调试信息。
Info :关键路径的信息,用于记录程序的正常操作。
Warn :警告信息,程序可以继续运行但可能会有问题。
Error :错误信息,程序发生错误但可以继续运行。
Fatal :严重错误信息,程序发生严重错误需要立即终止。
二、日志格式
建议使用标准的日志格式,便于解析和分析。示例如下:
[时间戳][日志级别][线程ID][类名.方法名]- 日志消息
三、日志内容
时间戳 :记录日志生成的时间,精确到毫秒。例如:
2024-06-06 12:34:56.789日志级别 :日志的严重性级别,例如:
INFO、ERROR线程ID :记录生成日志的线程ID,便于并发环境下的调试
类名.方法名 :记录生成日志的类名和方法名,便于定位代码
日志消息 :具体的日志信息,详细描述发生的事件
接下来讲解BeetleX是怎样去实现这个规范了,首先组件定义了一个日志记录接口
publicinterfaceILogHandler{voidWriteLog(LogLevel level, int threadid, string location, string model, string tag, string message, string stackTrace);}
一个非常简单写日志的方法,这个方法似乎使用起来也比较麻烦...那就简化一下它,定义一个结构来简化一些参数
publicstruct LogWriter{public LogLevel Level { get; set; }public ILogHandler Loger { get; set; }publicvoidWrite(EndPoint location, string model, string tag, string message) { Write(location?.ToString(), model, tag, message, null); }publicvoidWriteException(EndPoint location, string model, string tag, Exception e_) { Write(location?.ToString(), model, tag, e_.Message, e_.StackTrace); }publicvoidWrite(Socket location, string model, string tag, string message) { Write(location?.RemoteEndPoint?.ToString(), model, tag, message, null); }publicvoidWriteException(Socket location, string model, string tag, Exception e_) { Write(location?.RemoteEndPoint?.ToString(), model, tag, e_.Message, e_.StackTrace); }publicvoidWrite(ILocation context, string model, string tag, string message) { Write(context?.EndPoint?.ToString(), model, tag, message, null); }publicvoidWriteException(ILocation context, string model, string tag, Exception e_) { Write(context?.EndPoint?.ToString(), model, tag, e_.Message, e_.StackTrace); }publicvoidWrite(string location, string model, string tag, string message, string stackTrace) {if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(location)) location = "BeetleX"; Loger?.WriteLog(Level, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, location, model, tag, message, stackTrace); }}
通过这个结构写日志就简单多了,那这个日志记录结构如何获取呢?那针对它再定义一个接口
publicinterface IGetLogHandler : ILocation{ LogWriter? GetLoger(LogLevel type);}
这接口也只一个方法,根据日志级别返回上面定义的结构。在需要记录日志的类中实现一个这个方法
public LogWriter? GetLoger(LogLevel level){if ((int)(LogLevel) <= (int)level) { LogWriter result = new LogWriter(); result.Level = level; result.Loger = this;return result; }returnnull;}
方法还存在返回null的结构,外面使用每次都要判断一下似乎很麻烦!别忘记C#有先进的语法系统,看一下是如何使用的
publicoverridevoidWrite(byte[] buffer, int offset, int count){base.Write(buffer, offset, count); LogHandler?.GetLoger(LogLevel.Debug)?.Write(LogHandler, "BXSslStream", "SyncData", $"Write length {count}"); LogHandler?.GetLoger(Logs.LogLevel.Trace)?.Write(LogHandler, "BXSslStream", "✉ SyncData", $"Write {Convert.ToHexString(buffer, offset, count)}");}
用起来是不是很方便?比起多层判断再调用省事很多,一行代码即可。有了记录日志,那自然需要设计一个保存日志的。针对保存也设计一个接口
publicinterfaceILogOutputHandler{voidWrite(LogRecord log);voidFlush();}
接口也是很简单的,一个写日志记录方法和落盘的方法;针对Console实现的一扩展如下:
public classLogOutputToConsole : ILogOutputHandler{staticLogOutputToConsole() { Console.OutputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8; }publicLogOutputToConsole() { }static SingleThreadDispatcher<LogRecord> _dispatcher;public SingleThreadDispatcher<LogRecord> Dispatcher {get {if (_dispatcher != null)return _dispatcher;else {lock (typeof(LogOutputToConsole)) {if (_dispatcher == null) _dispatcher = new SingleThreadDispatcher<LogRecord>(OnWriteLog);return _dispatcher; } } } }static Task OnWriteLog(LogRecord e) { Console.Write($"[{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mmm:ss")}] ");switch (e.Level) {case LogLevel.Error: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkRed;break;case LogLevel.Warring: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;break;case LogLevel.Fatal: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;break;case LogLevel.Info: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;break;case LogLevel.Debug: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.DarkGray;break;default: Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;break; } Console.Write($"[{e.Level.ToString().PadLeft(7)}]"); Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray; Console.Write($" {e.ThreadID.ToString().PadLeft(3)} [{e.Location.PadRight(16)}{e.Model}{e.Tag.PadLeft(26 - e.Model.Length)}] {e.Message}");if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.StackTrace)) Console.Write($"\r\n\t\t{e.StackTrace}\r\n");else Console.Write("\r\n");return Task.CompletedTask; }publicvoidWrite(LogRecord log) { Dispatcher.Enqueue(log); }publicvoidFlush() { }}
以上BeetleX的日志功能就设计实现完成,并没有依赖于第三方,尽量不依赖第三方组件也是组件开始就已经明确的立场。接下来看一下组件的详细日志细化到什么样的程度。
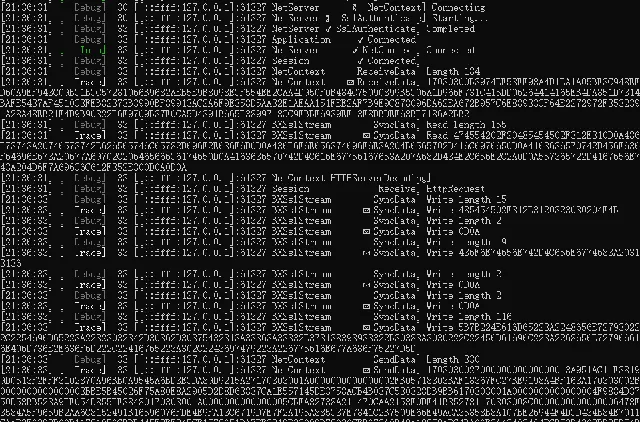
疑问 :有人可以会问在这核心组件存在这么多记录日志的代码会影响组件的整体性能吗?其实当Level不符合要求的时候后面记录日志方法的调用都不会存在,所以单凭这个 Level值判断是不会对组件有性能上的影响的。当然日志输出时刷于大量信息输出记录肯定会影响到整体性能,具体还是根据情况来制定Level的输出。
BeetleX
开源跨平台通讯框架(支持TLS)
提供HTTP,Websocket,MQTT,Redis,RPC和服务网关开源组件
个人微信:henryfan128 QQ:28304340
有丰富的高吐网络服务设计经验
关注公众号
https://github.com/beetlex-io/












