最新激活码来了 (支持所有版本,非破解)
提取地址:
https://www.ajihuo.com
👇SpringBoot+Vue完整源码免费分享👇
(源码+搭建教程+可商用)
源码
👆源码会持续更新,加油哦!👆
作者:老鹰汤
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7156439842958606349
线上事故回顾
前段时间新增一个特别简单的功能,晚上上线前review代码时想到公司拼搏进取的价值观临时加一行log日志,觉得就一行简单的日志基本上没啥问题,结果刚上完线后一堆报警,赶紧回滚了代码,找到问题删除了添加日志的代码,重新上线完毕。
情景还原
定义了一个 CountryDTO
public classCountryDTO{private String country;public void setCountry(String country) {this.country = country; }public String getCountry() {returnthis.country; }publicBoolean isChinaName() {returnthis.country.equals("中国"); }}
定义测试类 FastJonTest
public classFastJonTest { @TestpublicvoidtestSerialize() { CountryDTO countryDTO = new CountryDTO(); String str = JSON.toJSONString(countryDTO); System.out.println(str); }}
运行时报空指针错误:
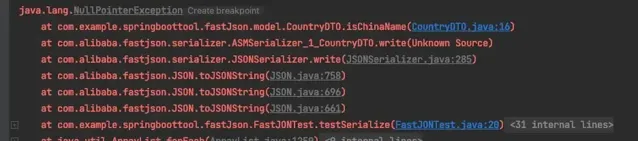
通过报错信息可以看出来是 序列化的过程中执行了 isChinaName()方法,这时候this.country变量为空, 那么问题来了:
序列化为什么会执行isChinaName()呢?
引申一下,序列化过程中会执行那些方法呢?
源码分析
通过debug观察调用链路的堆栈信息
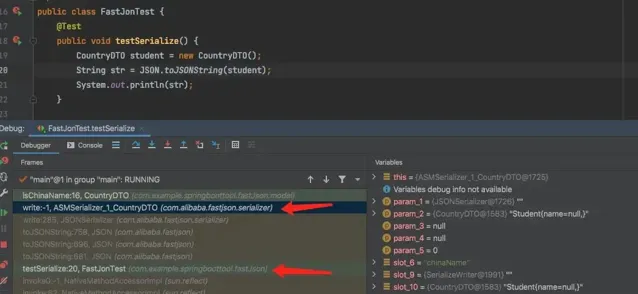
调用链中的ASMSerializer_1_CountryDTO.write是FastJson使用asm技术动态生成了一个类ASMSerializer_1_CountryDTO,
asm技术其中一项使用场景就是通过到动态生成类用来代替java反射,从而避免重复执行时的反射开销
JavaBeanSerizlier序列化原理
通过下图看出序列化的过程中,主要是调用JavaBeanSerializer类的write()方法。
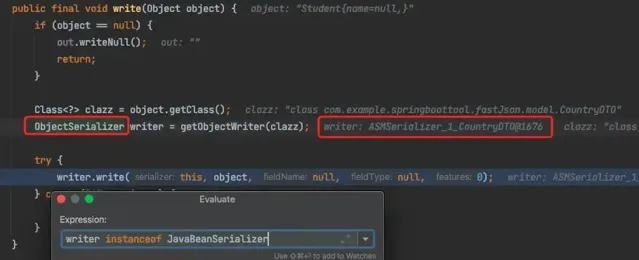
而JavaBeanSerializer 主要是通过 getObjectWriter()方法获取,通过对getObjectWriter()执行过程的调试,找到比较关键的com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeConfig#createJavaBeanSerializer方法,进而找到 com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#computeGetters
public static List<FieldInfo> computeGetters( class<?> clazz, // JSONType jsonType, // Map<String,String> aliasMap, // Map<String,Field> fieldCacheMap, // boolean sorted, // PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy // ){//省略部分代码.... Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();for(Method method : methods){//省略部分代码...if(method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)){continue; }if(method.getParameterTypes().length != 0){continue; }//省略部分代码... JSONField annotation = TypeUtils.getAnnotation(method, JSONField. class);//省略部分代码...if(annotation != null){if(!annotation.serialize()){continue; }if(annotation.name().length() != 0){//省略部分代码... } }if(methodName.startsWith("get")){//省略部分代码... }if(methodName.startsWith("is")){//省略部分代码... } }}
从代码中大致分为三种情况:
@JSONField(.serialize = false, name = "xxx")注解
getXxx() : get开头的方法
isXxx():is开头的方法
序列化流程图
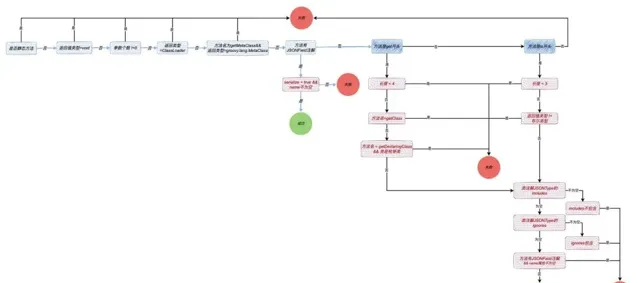
示例代码
/** * case1: @JSONField(serialize = false) * case2: getXxx()返回值为void * case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型 * case4: @JSONType(ignores = "xxx") */@JSONType(ignores = "otherName")public classCountryDTO {private String country;publicvoidsetCountry(String country) {this.country = country; }public String getCountry() {returnthis.country; }publicstaticvoidqueryCountryList() { System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!"); }public Boolean isChinaName() { System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");returntrue; }public String getEnglishName() { System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");return"lucy"; }public String getOtherName() { System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");return"lucy"; }/** * case1: @JSONField(serialize = false) */ @JSONField(serialize = false)public String getEnglishName2() { System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");return"lucy"; }/** * case2: getXxx()返回值为void */publicvoidgetEnglishName3() { System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!"); }/** * case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型 */public String isChinaName2() { System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");return"isChinaName2"; }}
运行结果为:
isChinaName()执行!!getEnglishName()执行!!{"chinaName":true,"englishName":"lucy"}
代码规范
可以看出来序列化的规则还是很多的,比如有时需要关注返回值,有时需要关注参数个数,有时需要关注@JSONType注解,有时需要关注@JSONField注解;当一个事物的判别方式有多种的时候,由于团队人员掌握知识点的程度不一样,这个方差很容易导致代码问题,所以尽量有一种推荐方案。这里推荐使用@JSONField(serialize = false)来显式的标注方法不参与序列化,下面是使用推荐方案后的代码,是不是一眼就能看出来哪些方法不需要参与序列化了。
public classCountryDTO{private String country;public void setCountry(String country) {this.country = country; }public String getCountry() {returnthis.country; }@JSONField(serialize = false)public static void queryCountryList() { System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!"); }publicBoolean isChinaName() { System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");returntrue; }public String getEnglishName() { System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");return"lucy"; }@JSONField(serialize = false)public String getOtherName() { System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");return"lucy"; }@JSONField(serialize = false)public String getEnglishName2() { System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");return"lucy"; }@JSONField(serialize = false)public void getEnglishName3() { System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!"); }@JSONField(serialize = false)public String isChinaName2() { System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");return"isChinaName2"; }}
三个频率高的序列化的情况
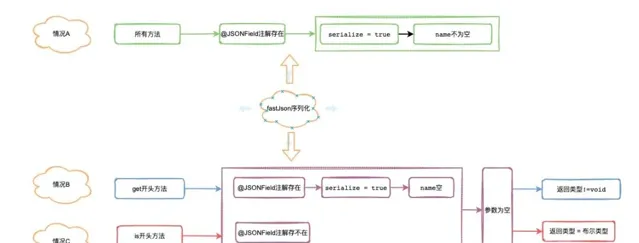
以上流程基本遵循 发现问题 --> 原理分析 --> 解决问题 --> 升华(编程规范)。
围绕业务上:解决问题 -> 如何选择一种好的额解决方案 -> 好的解决方式如何扩展n个系统应用;
围绕技术上:解决单个问题,顺着单个问题掌握这条线上的原理。











