
👉 欢迎 ,你将获得: 专属的项目实战 / Java 学习路线 / 一对一提问 / 学习打卡 / 赠书福利
全栈前后端分离博客项目 2.0 版本完结啦, 演示链接 : http://116.62.199.48/ , 新项目正在酝酿中 。全程手摸手,后端 + 前端全栈开发,从 0 到 1 讲解每个功能点开发步骤,1v1 答疑,直到项目上线。 目前已更新了239小节,累计38w+字,讲解图:1645张,还在持续爆肝中.. 后续还会上新更多项目,目标是将Java领域典型的项目都整一波,如秒杀系统, 在线商城, IM即时通讯,Spring Cloud Alibaba 等等,
场景说明
模拟数据
场景分析
读取数据
处理数据
思路一:通过单线程处理
思路二:分治法
遇到的问题
场景说明
现有一个 10G 文件的数据,里面包含了 18-70 之间的整数,分别表示 18-70 岁的人群数量统计,假设年龄范围分布均匀,分别表示系统中所有用户的年龄数,找出重复次数最多的那个数,现有一台内存为 4G、2 核 CPU 的电脑,请写一个算法实现。
23,31,42,19,60,30,36,........
模拟数据
Java 中一个整数占 4 个字节,模拟 10G 为 30 亿左右个数据, 采用追加模式写入 10G 数据到硬盘里。每 100 万个记录写一行,大概 4M 一行,10G 大概 2500 行数据。
package bigdata;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @Desc:
* @Author: bingbing
* @Date: 2022/5/4 0004 19:05
*/
public class GenerateData {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static int generateRandomData(int start, int end) {
return random.nextInt(end - start + 1) + start;
}
/**
* 产生10G的 1-1000的数据在D盘
*/
public void generateData() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\ User.dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int start = 18;
int end = 70;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
BufferedWriter bos = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file, true)));
for (long i = 1; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE * 1.7; i++) {
String data = generateRandomData(start, end) + ",";
bos.write(data);
// 每100万条记录成一行,100万条数据大概4M
if (i % 1000000 == 0) {
bos.write("\n");
}
}
System.out.println("写入完成! 共花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + " s");
bos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenerateData generateData = new GenerateData();
try {
generateData.generateData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
上述代码调整参数执行 2 次,凑 10 个 G 的数据在 D 盘的 User.dat 文件里。
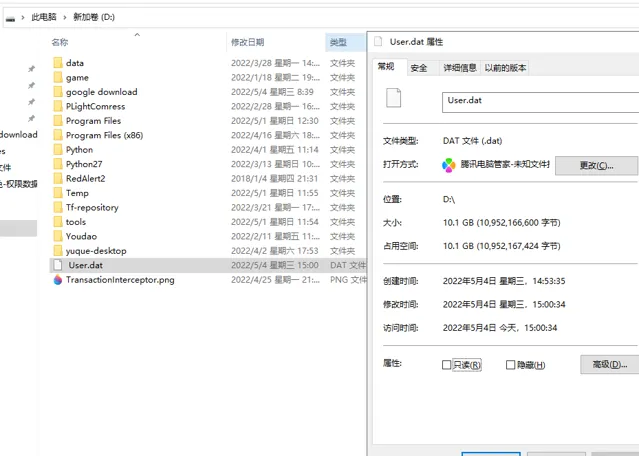
准备好 10G 数据后,接着写如何处理这些数据。
场景分析
10G 的数据比当前拥有的运行内存大的多,不能全量加载到内存中读取,如果采用全量加载,那么内存会直接爆掉,只能按行读取,Java 中的 bufferedReader 的 readLine() 按行读取文件里的内容。
读取数据
首先我们写一个方法单线程读完这 30E 数据需要多少时间,每读 100 行打印一次:
private static void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取
// SplitData.splitLine(line);
if (count % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("读取100行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
System.gc();
}
count++;
}
running = false;
br.close();
}
按行读完 10G 的数据大概 20 秒,基本每 100 行,1E 多数据花 1S,速度还挺快:

处理数据
思路一:通过单线程处理
通过单线程处理,初始化一个 countMap,key 为年龄,value 为出现的次数,将每行读取到的数据按照 "," 进行分割,然后获取到的每一项进行保存到 countMap 里,如果存在,那么值 key 的 value+1。
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
try {
File subFile = new File(dir + "\" + i + ".dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
subFile.createNewFile();
}
countMap.computeIfAbsent(i + "", integer -> new AtomicInteger(0));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
单线程读取并统计 countMap:
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
String[] arr = lineData.split(",");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
countMap.computeIfAbsent(str, s -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}
通过比较找出年龄数最多的年龄并打印出来:
private static void findMostAge() {
Integer targetValue = 0;
String targetKey = null;
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger>> entrySetIterator = countMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entrySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> entry = entrySetIterator.next();
Integer value = entry.getValue().get();
String key = entry.getKey();
if (value > targetValue) {
targetValue = value;
targetKey = key;
}
}
System.out.println("数量最多的年龄为:" + targetKey + "数量为:" + targetValue);
}
完整代码:
package bigdata;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @Desc:
* @Author: bingbing
* @Date: 2022/5/4 0004 19:19
* 单线程处理
*/
public class HandleMaxRepeatProblem_v0 {
public static final int start = 18;
public static final int end = 70;
public static final String dir = "D:\dataDir";
public static final String FILE_NAME = "D:\ User.dat";
/**
* 统计数量
*/
private static Map<String, AtomicInteger> countMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 开启消费的标志
*/
private static volatile boolean startConsumer = false;
/**
* 消费者运行保证
*/
private static volatile boolean consumerRunning = true;
/**
* 按照 "," 分割数据,并写入到countMap里
*/
static class SplitData {
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
String[] arr = lineData.split(",");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
countMap.computeIfAbsent(str, s -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}
}
/**
* init map
*/
static {
File file = new File(dir);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
try {
File subFile = new File(dir + "\" + i + ".dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
subFile.createNewFile();
}
countMap.computeIfAbsent(i + "", integer -> new AtomicInteger(0));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
readData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
private static void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取,并向map里写入数据
SplitData.splitLine(line);
if (count % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("读取100行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count++;
}
findMostAge();
br.close();
}
private static void findMostAge() {
Integer targetValue = 0;
String targetKey = null;
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger>> entrySetIterator = countMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entrySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> entry = entrySetIterator.next();
Integer value = entry.getValue().get();
String key = entry.getKey();
if (value > targetValue) {
targetValue = value;
targetKey = key;
}
}
System.out.println("数量最多的年龄为:" + targetKey + "数量为:" + targetValue);
}
private static void clearTask() {
// 清理,同时找出出现字符最大的数
findMostAge();
System.exit(-1);
}
}
测试结果: 总共花了 3 分钟读取完并统计完所有数据。
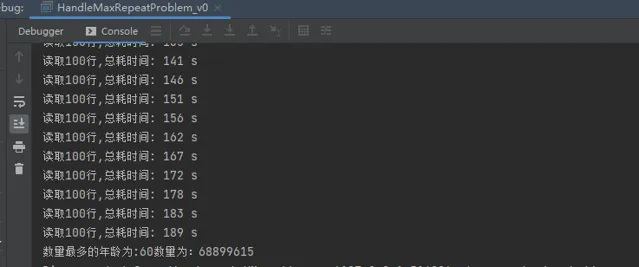
内存消耗为 2G-2.5G,CPU 利用率太低,只向上浮动了 20%-25% 之间:

要想提高 CPU 的利用率,那么可以使用多线程去处理。下面我们使用多线程去解决这个 CPU 利用率低的问题。
思路二:分治法
使用多线程去消费读取到的数据。采用生产者、消费者模式去消费数据,因为在读取的时候是比较快的,单线程的数据处理能力比较差,因此思路一的性能阻塞在取数据方,又是同步的,所以导致整个链路的性能会变的很差。
所谓分治法就是分而治之,也就是说将海量数据分割处理。根据 CPU 的能力初始化 n 个线程,每一个线程去消费一个队列,这样线程在消费的时候不会出现抢占队列的问题。
同时为了保证线程安全和生产者消费者模式的完整,采用阻塞队列,Java 中提供了 LinkedBlockingQueue 就是一个阻塞队列。
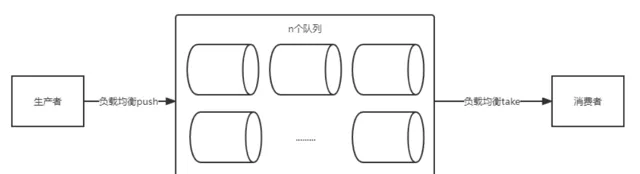
①初始化阻塞队列
使用 linkedList 创建一个阻塞队列列表:
private static List<LinkedBlockingQueue<String>> blockQueueLists = new LinkedList<>();
在 static 块里初始化阻塞队列的数量和单个阻塞队列的容量为 256,上面讲到了 30E 数据大概 2500 行,按行塞到队列里,20 个队列,那么每个队列 125 个,因此可以容量可以设计为 256 即可:
//每个队列容量为256
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
blockQueueLists.add(new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(256));
}
②生产者
为了实现负载的功能, 首先定义一个 count 计数器,用来记录行数:
private static AtomicLong count = new AtomicLong(0);
按照行数来计算队列的下标:long index=count.get()%threadNums。
下面算法就实现了对队列列表中的队列进行轮询的投放:
static class SplitData {
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
// System.out.println(lineData.length());
String[] arr = lineData.split("\n");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
long index = count.get() % threadNums;
try {
// 如果满了就阻塞
blockQueueLists.get((int) index).put(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count.getAndIncrement();
}
}
③消费者
队列线程私有化: 消费方在启动线程的时候根据 index 去获取到指定的队列,这样就实现了队列的线程私有化。
private static void startConsumer() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
//如果共用一个队列,那么线程不宜过多,容易出现抢占现象
System.out.println("开始消费...");
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
final int index = i;
// 每一个线程负责一个queue,这样不会出现线程抢占队列的情况。
new Thread(() -> {
while (consumerRunning) {
startConsumer = true;
try {
String str = blockQueueLists.get(index).take();
countNum(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
多子线程分割字符串: 由于从队列中多到的字符串非常的庞大,如果又是用单线程调用 split(",") 去分割,那么性能同样会阻塞在这个地方。
// 按照arr的大小,运用多线程分割字符串
private static void countNum(String str) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
arr[1] = str.length() / 3;
// System.out.println("分割的字符串为start位置为:" + arr[0] + ",end位置为:" + arr[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final String innerStr = SplitData.splitStr(str, arr);
// System.out.println("分割的字符串为start位置为:" + arr[0] + ",end位置为:" + arr[1]);
new Thread(() -> {
String[] strArray = innerStr.split(",");
for (String s : strArray) {
countMap.computeIfAbsent(s, s1 -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}).start();
}
}
分割字符串算法: 分割时从 0 开始,按照等分的原则,将字符串 n 等份,每一个线程分到一份。
用一个 arr 数组的 arr[0] 记录每次的分割开始位置,arr[1] 记录每次分割的结束位置,如果遇到的开始的字符不为 ",",那么就 startIndex-1,如果结束的位置不为 ",",那么将 endIndex 向后移一位。
如果 endIndex 超过了字符串的最大长度,那么就把最后一个字符赋值给 arr[1]。
/**
* 按照 x坐标 来分割 字符串,如果切到的字符不为「,」, 那么把坐标向前或者向后移动一位。
*
* @param line
* @param arr 存放x1,x2坐标
* @return
*/
public static String splitStr(String line, int[] arr) {
int startIndex = arr[0];
int endIndex = arr[1];
char start = line.charAt(startIndex);
char end = line.charAt(endIndex);
if ((startIndex == 0 || start == ',') && end == ',') {
arr[0] = endIndex + 1;
arr[1] = arr[0] + line.length() / 3;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return line.substring(startIndex, endIndex);
}
if (startIndex != 0 && start != ',') {
startIndex = startIndex - 1;
}
if (end != ',') {
endIndex = endIndex + 1;
}
arr[0] = startIndex;
arr[1] = endIndex;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return splitStr(line, arr);
}
完整代码:
package bigdata;
import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollectionUtil;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Desc:
* @Author: bingbing
* @Date: 2022/5/4 0004 19:19
* 多线程处理
*/
public class HandleMaxRepeatProblem {
public static final int start = 18;
public static final int end = 70;
public static final String dir = "D:\dataDir";
public static final String FILE_NAME = "D:\ User.dat";
private static final int threadNums = 20;
/**
* key 为年龄, value为所有的行列表,使用队列
*/
private static Map<Integer, Vector<String>> valueMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 存放数据的队列
*/
private static List<LinkedBlockingQueue<String>> blockQueueLists = new LinkedList<>();
/**
* 统计数量
*/
private static Map<String, AtomicInteger> countMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static Map<Integer, ReentrantLock> lockMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 队列负载均衡
private static AtomicLong count = new AtomicLong(0);
/**
* 开启消费的标志
*/
private static volatile boolean startConsumer = false;
/**
* 消费者运行保证
*/
private static volatile boolean consumerRunning = true;
/**
* 按照 "," 分割数据,并写入到文件里
*/
static class SplitData {
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
// System.out.println(lineData.length());
String[] arr = lineData.split("\n");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
long index = count.get() % threadNums;
try {
// 如果满了就阻塞
blockQueueLists.get((int) index).put(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count.getAndIncrement();
}
}
/**
* 按照 x坐标 来分割 字符串,如果切到的字符不为「,」, 那么把坐标向前或者向后移动一位。
*
* @param line
* @param arr 存放x1,x2坐标
* @return
*/
public static String splitStr(String line, int[] arr) {
int startIndex = arr[0];
int endIndex = arr[1];
char start = line.charAt(startIndex);
char end = line.charAt(endIndex);
if ((startIndex == 0 || start == ',') && end == ',') {
arr[0] = endIndex + 1;
arr[1] = arr[0] + line.length() / 3;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return line.substring(startIndex, endIndex);
}
if (startIndex != 0 && start != ',') {
startIndex = startIndex - 1;
}
if (end != ',') {
endIndex = endIndex + 1;
}
arr[0] = startIndex;
arr[1] = endIndex;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return splitStr(line, arr);
}
public static void splitLine0(String lineData) {
String[] arr = lineData.split(",");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
int keyIndex = Integer.parseInt(str);
ReentrantLock lock = lockMap.computeIfAbsent(keyIndex, lockMap -> new ReentrantLock());
lock.lock();
try {
valueMap.get(keyIndex).add(str);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
// boolean wait = true;
// for (; ; ) {
// if (!lockMap.get(Integer.parseInt(str)).isLocked()) {
// wait = false;
// valueMap.computeIfAbsent(Integer.parseInt(str), integer -> new Vector<>()).add(str);
// }
// // 当前阻塞,直到释放锁
// if (!wait) {
// break;
// }
// }
}
}
}
/**
* init map
*/
static {
File file = new File(dir);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
//每个队列容量为256
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
blockQueueLists.add(new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(256));
}
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
try {
File subFile = new File(dir + "\" + i + ".dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
subFile.createNewFile();
}
countMap.computeIfAbsent(i + "", integer -> new AtomicInteger(0));
// lockMap.computeIfAbsent(i, lock -> new ReentrantLock());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 读取数据
readData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 开始消费
startConsumer();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
// 监控
monitor();
}).start();
}
/**
* 每隔60s去检查栈是否为空
*/
private static void monitor() {
AtomicInteger emptyNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
while (consumerRunning) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (startConsumer) {
// 如果所有栈的大小都为0,那么终止进程
AtomicInteger emptyCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
if (blockQueueLists.get(i).size() == 0) {
emptyCount.getAndIncrement();
}
}
if (emptyCount.get() == threadNums) {
emptyNum.getAndIncrement();
// 如果连续检查指定次数都为空,那么就停止消费
if (emptyNum.get() > 12) {
consumerRunning = false;
System.out.println("消费结束...");
try {
clearTask();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getCause());
} finally {
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
}
}
}
private static void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取,并向队列写入数据
SplitData.splitLine(line);
if (count % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("读取100行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.gc();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count++;
}
br.close();
}
private static void clearTask() {
// 清理,同时找出出现字符最大的数
Integer targetValue = 0;
String targetKey = null;
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger>> entrySetIterator = countMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entrySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> entry = entrySetIterator.next();
Integer value = entry.getValue().get();
String key = entry.getKey();
if (value > targetValue) {
targetValue = value;
targetKey = key;
}
}
System.out.println("数量最多的年龄为:" + targetKey + "数量为:" + targetValue);
System.exit(-1);
}
/**
* 使用linkedBlockQueue
*
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
*/
private static void startConsumer() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
//如果共用一个队列,那么线程不宜过多,容易出现抢占现象
System.out.println("开始消费...");
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
final int index = i;
// 每一个线程负责一个queue,这样不会出现线程抢占队列的情况。
new Thread(() -> {
while (consumerRunning) {
startConsumer = true;
try {
String str = blockQueueLists.get(index).take();
countNum(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
// 按照arr的大小,运用多线程分割字符串
private static void countNum(String str) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
arr[1] = str.length() / 3;
// System.out.println("分割的字符串为start位置为:" + arr[0] + ",end位置为:" + arr[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final String innerStr = SplitData.splitStr(str, arr);
// System.out.println("分割的字符串为start位置为:" + arr[0] + ",end位置为:" + arr[1]);
new Thread(() -> {
String[] strArray = innerStr.split(",");
for (String s : strArray) {
countMap.computeIfAbsent(s, s1 -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}).start();
}
}
/**
* 后台线程去消费map里数据写入到各个文件里, 如果不消费,那么会将内存程爆
*/
private static void startConsumer0() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
final int index = i;
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(dir + "\" + i + ".dat", false), "utf-8"));
new Thread(() -> {
int miss = 0;
int countIndex = 0;
while (true) {
// 每隔100万打印一次
int count = countMap.get(index).get();
if (count > 1000000 * countIndex) {
System.out.println(index + "岁年龄的个数为:" + countMap.get(index).get());
countIndex += 1;
}
if (miss > 1000) {
// 终止线程
try {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
Vector<String> lines = valueMap.computeIfAbsent(index, vector -> new Vector<>());
// 写入到文件里
try {
if (CollectionUtil.isEmpty(lines)) {
miss++;
Thread.sleep(1000);
} else {
// 100个一批
if (lines.size() < 1000) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
continue;
}
// 1000个的时候开始处理
ReentrantLock lock = lockMap.computeIfAbsent(index, lockIndex -> new ReentrantLock());
lock.lock();
try {
Iterator<String> iterator = lines.iterator();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
sb.append(iterator.next());
countMap.get(index).addAndGet(1);
}
try {
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 清除掉vector
valueMap.put(index, new Vector<>());
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
测试结果:
内存和 CPU 初始占用大小:

启动后,运行时稳定在 11.7,CPU 稳定利用在 90% 以上。
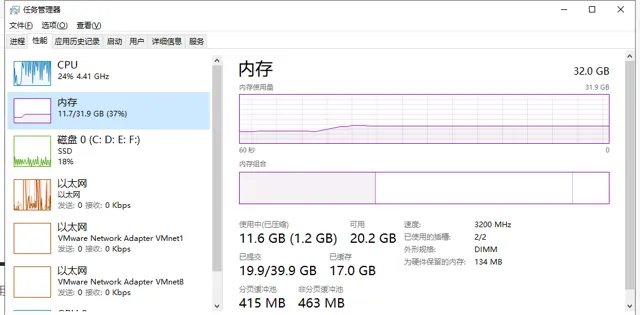
总耗时由 180S 缩减到 103S,效率提升 75%,得到的结果也与单线程处理的一致!
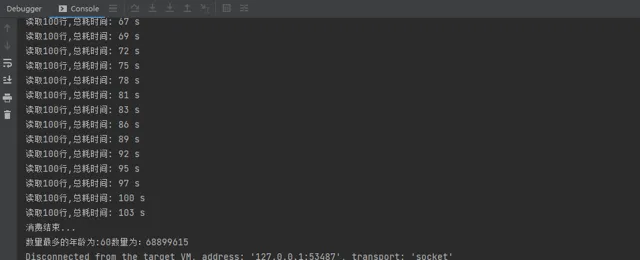
遇到的问题
如果在运行了的时候,发现 GC 突然罢工了,开始不工作了,有可能是 JVM 的堆中存在的垃圾太多,没回收导致内存的突增。
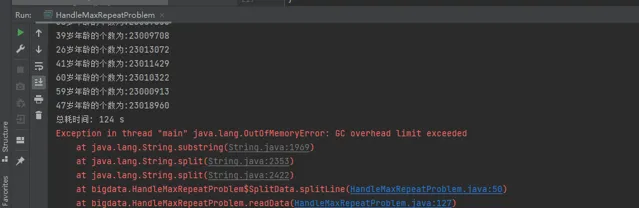
解决方法:在读取一定数量后,可以让主线程暂停几秒,手动调用 GC。
提示:本 demo 的线程创建都是手动创建的,实际开发中使用的是线程池!
👉 欢迎 ,你将获得: 专属的项目实战 / Java 学习路线 / 一对一提问 / 学习打卡 / 赠书福利
全栈前后端分离博客项目 2.0 版本完结啦, 演示链接 : http://116.62.199.48/ , 新项目正在酝酿中 。全程手摸手,后端 + 前端全栈开发,从 0 到 1 讲解每个功能点开发步骤,1v1 答疑,直到项目上线。 目前已更新了239小节,累计38w+字,讲解图:1645张,还在持续爆肝中.. 后续还会上新更多项目,目标是将Java领域典型的项目都整一波,如秒杀系统, 在线商城, IM即时通讯,Spring Cloud Alibaba 等等,

1.
2.
3.
4.
最近面试BAT,整理一份面试资料【Java面试BATJ通关手册】,覆盖了Java核心技术、JVM、Java并发、SSM、微服务、数据库、数据结构等等。
获取方式:点「在看」,关注公众号并回复 Java 领取,更多内容陆续奉上。
PS:因公众号平台更改了推送规则,如果不想错过内容,记得读完点一下「在看」,加个「星标」,这样每次新文章推送才会第一时间出现在你的订阅列表里。
点「在看」支持小哈呀,谢谢啦











