前言
我們在使用
ASP.NET Core WebApi
時它支持使用指定的輸入和輸出格式來交換數據。輸入數據靠模型繫結的機制處理,輸出數據則需要用格式化的方式進行處理。
ASP.NET Core
框架已經內建了處理
JSON
和
XML
的輸入和輸出方式,預設的情況我們送出
JSON
格式的內容,它可以自行進行模型繫結,也可以把物件型別的返回值輸出成
JSON
格式,這都歸功於內建的
JSON
格式化程式。本篇文章我們將透過自訂一個
YAML
格式的轉換器開始,逐步了解它到底是如何工作的。以及透過內建的
JSON
格式化輸入輸出源碼,加深對
Formatter
程式的了解。
自訂開始
要想先了解
Formatter
的工作原理,當然需要從自訂開始。因為一般自訂的時候我們一般會選用自己最簡單最擅長的方式去擴充套件,然後逐步完善加深理解。格式化器分為兩種,一種是用來處理輸入數據格式的
InputFormatter
,另一種是用來處理返回數據格式的
OutputFormatter
。本篇文章範例,我們從自訂
YAML
格式的轉換器開始。因為目前
YAML
格式確實比較流行,得益於它簡單明了的格式,目前也有很多中介軟體都是用
YAML
格式。這裏我們使用的是
YamlDotNet
這款元件,具體的引入資訊如下所示
<PackageReference Include="YamlDotNet" Version="15.1.0" />
YamlInputFormatter
首先我們來看一下自訂請求數據的格式化也就是
InputFormatter
,它用來處理了請求數據的格式,也就是我們在
Http請求體
裏的數據格式如何處理,手下我們需要定義個
YamlInputFormatter
類,繼承自
TextInputFormatter
抽象類
public classYamlInputFormatter : TextInputFormatter
{
privatereadonly IDeserializer _deserializer;
publicYamlInputFormatter(DeserializerBuilder deserializerBuilder)
{
_deserializer = deserializerBuilder.Build();
//添加與之繫結的MediaType,這裏其實繫結的送出的ContentType的值
//如果請求ContentType:text/yaml或ContentType:text/yml才能命中該YamlInputFormatter
SupportedMediaTypes.Add(MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse("text/yaml"));
SupportedMediaTypes.Add(MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse("text/yml"));
//添加編碼型別比如application/json;charset=UTF-8後面的這種charset
SupportedEncodings.Add(Encoding.UTF8);
SupportedEncodings.Add(Encoding.Unicode);
}
publicoverrideasync Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadRequestBodyAsync(InputFormatterContext context, Encoding encoding)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(context);
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(encoding);
//獲取請求Body
var readStream = context.HttpContext.Request.Body;
object? model;
try
{
TextReader textReader = new StreamReader(readStream);
//獲取Action參數型別
var type = context.ModelType;
//把yaml字串轉換成具體的物件
model = _deserializer.Deserialize(textReader, type);
}
catch (YamlException ex)
{
context.ModelState.TryAddModelError(context.ModelName, ex.Message);
thrownew InputFormatterException("反序列化輸入數據時出錯\n\n", ex.InnerException!);
}
if (model == null && !context.TreatEmptyInputAsDefaultValue)
{
return InputFormatterResult.NoValue();
}
else
{
return InputFormatterResult.Success(model);
}
}
}
這裏需要註意的是配置
SupportedMediaTypes
,也就是添加與
YamlInputFormatter
繫結的
MediaType
,也就是我們請求時設定的
Content-Type
的值,這個配置是必須要的,否則沒辦法判斷當前
YamlInputFormatter
與哪種
Content-Type
進行繫結。接下來定義完了之後如何把它接入程式使用它呢?也很簡單在
MvcOptions
中配置即可,如下所示
builder.Services.AddControllers(options => {
options.InputFormatters.Add(new YamlInputFormatter(new DeserializerBuilder()));
});
接下來我們定義一個簡單型別和Action來演示一下,類和程式碼不具備任何實際意義,只是為了演示
[HttpPost("AddAddress")]
public Address AddAddress(Address address)
{
return address;
}
public classAddress
{
publicstring City { get; set; }
publicstring Country { get; set; }
publicstring Phone { get; set; }
publicstring ZipCode { get; set; }
public List<string> Tags { get; set; }
}
我們用
Postman
測試一下,送出一個
yaml
型別的格式,效果如下所示
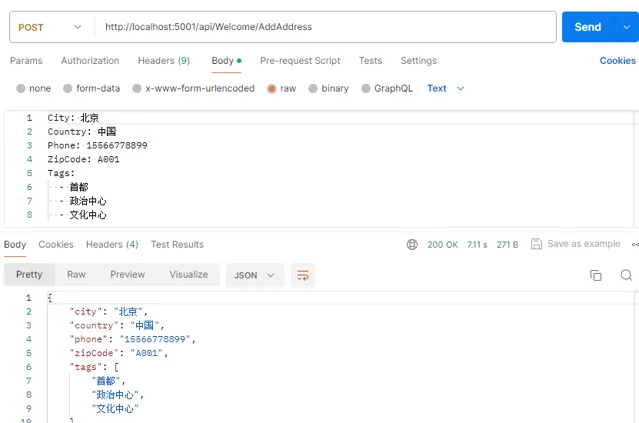
這裏需要註意的是我們需要在
Postman
中設定
Content-Type
為
text/yml
或
text/yaml
YamlOutputFormatter
上面我們演示了如何定義
InputFormatter
它的作用是將請求的數據格式化成具體型別。無獨有偶,既然請求數據格式可以定義,那麽輸出的數據格式同樣可以定義,這裏就需要用到
OutputFormatter
。接下來我們定義一個
YamlOutputFormatter
繼承自
TextOutputFormatter
抽象類,程式碼如下所示
public classYamlOutputFormatter : TextOutputFormatter
{
privatereadonly ISerializer _serializer;
publicYamlOutputFormatter(SerializerBuilder serializerBuilder)
{
//添加與之繫結的MediaType,這裏其實繫結的送出的Accept的值
//如果請求Accept:text/yaml或Accept:text/yml才能命中該YamlOutputFormatter
SupportedMediaTypes.Add(MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse("text/yaml"));
SupportedMediaTypes.Add(MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse("text/yml"));
SupportedEncodings.Add(Encoding.UTF8);
SupportedEncodings.Add(Encoding.Unicode);
_serializer = serializerBuilder.Build();
}
publicoverrideboolCanWriteResult(OutputFormatterCanWriteContext context)
{
//什麽條件可以使用yaml結果輸出,至於為什麽要重寫CanWriteResult方法,我們在後面分析源碼的時候會解釋
string accept = context.HttpContext.Request.Headers.Accept.ToString() ?? "";
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(accept))
{
returnfalse;
}
var parsedContentType = new MediaType(accept);
for (var i = 0; i < SupportedMediaTypes.Count; i++)
{
var supportedMediaType = new MediaType(SupportedMediaTypes[i]);
if (parsedContentType.IsSubsetOf(supportedMediaType))
{
returntrue;
}
}
returnfalse;
}
publicoverrideasync Task WriteResponseBodyAsync(OutputFormatterWriteContext context, Encoding selectedEncoding)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(context);
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(selectedEncoding);
try
{
var httpContext = context.HttpContext;
//獲取輸出的物件,轉成成yaml字串並輸出
string respContent = _serializer.Serialize(context.Object);
await httpContext.Response.WriteAsync(respContent);
}
catch (YamlException ex)
{
thrownew InputFormatterException("序列化輸入數據時出錯\n\n", ex.InnerException!);
}
}
}
同樣的這裏我們也添加了
SupportedMediaTypes
的值,它的作用是我們請求時設定的
Accept
的值,這個配置也是必須要的,也就是請求的頭中為
Accept:text/yaml
或
Accept:text/yml
才能命中該
YamlOutputFormatter
。配置的時候同樣也在
MvcOptions
中配置即可
builder.Services.AddControllers(options => {
options.OutputFormatters.Add(new YamlOutputFormatter(new SerializerBuilder()));
});
接下來我們同樣還是使用上面的程式碼進行演示,只是我們這裏更換一下重新設定一下相關Header即可,這次我們直接送出
json
型別的數據,它會輸出
yaml
格式,程式碼什麽的完全不用變,結果如下所示
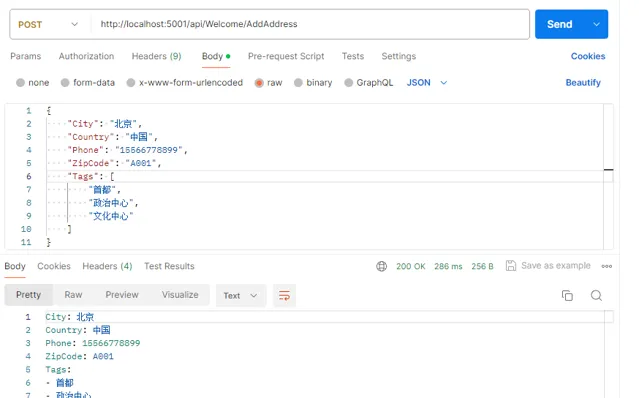
這裏需要註意的請求頭的設定發生了變化
小結
上面我們講解了控制請求數據格式的
TextInputFormatter
和控制輸出格式的
TextOutputFormatter
。其中
InputFormatter
負責給
ModelBinding
輸送型別物件,
OutputFormatter
負責給
ObjectResult
輸出值,這我們可以看到它們只能控制
WebAPI
中
Controller/Action
的且返回
ObjectResult
的這種情況才生效,其它的比如
MinimalApi
、
GRPC
是起不到效果的。透過上面的範例,有同學心裏可能會存在疑問,上面在
AddControllers
方法中註冊
TextInputFormatter
和
TextOutputFormatter
的時候,沒辦法完成註入的服務,比如如果
YamlInputFormatter
或
YamlOutputFormatter
構造例項的時候無法獲取
DI容器
中的例項。確實,如果使用上面的方式我們確實沒辦法完成這個需求,不過我們可以透過其它方法實作,那就是去擴充套件
MvcOptions
選項,實作如下所示
public classYamlMvcOptionsSetup : IConfigureOptions<MvcOptions>
{
privatereadonly ILoggerFactory _loggerFactory;
publicYamlMvcOptionsSetup(ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
_loggerFactory = loggerFactory;
}
publicvoidConfigure(MvcOptions options)
{
var yamlInputLogger = _loggerFactory.CreateLogger<YamlInputFormatter>();
options.InputFormatters.Add(new YamlInputFormatter(new DeserializerBuilder()));
var yamlOutputLogger = _loggerFactory.CreateLogger<YamlOutputFormatter>();
options.OutputFormatters.Add(new YamlOutputFormatter(new SerializerBuilder()));
}
}
我們定義了
YamlMvcOptionsSetup
去擴充套件
MvcOptions
選項,然後我們將
YamlMvcOptionsSetup
註冊到容器即可
builder.Services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Transient<IConfigureOptions<MvcOptions>, YamlMvcOptionsSetup>());
探究工作方式
上面我們演示了如何自訂
InputFormatter
和
OutputFormatter
,也講解了
InputFormatter
負責給
ModelBinding
輸送型別物件,
OutputFormatter
負責給
ObjectResult
輸出值。接下來我們就透過閱讀其中的源碼來看一下
InputFormatter
和
OutputFormatter
是如何工作來影響
模型繫結
和
ObjectResult
的結果。
需要註意的是!我們展示的源碼是刪減過的,只關註我們需要關註的地方,因為源碼中涉及的內容太多,不方便觀看,所以只保留我們關註的地方,還望諒解。
TextInputFormatter如何工作
上面我們看到了
YamlInputFormatter
是繼承了
TextInputFormatter
抽象類,並重寫了
ReadRequestBodyAsync
方法。接下來我們就從
TextInputFormatter
的
ReadRequestBodyAsync
方法來入手,我們來看一下源碼定義[
點選檢視TextInputFormatter源碼👈
[1]
]
publicabstract classTextInputFormatter : InputFormatter
{
public IList<Encoding> SupportedEncodings { get; } = new List<Encoding>();
publicoverride Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadRequestBodyAsync(InputFormatterContext context)
{
//判斷Encoding是否符合我們設定的SupportedEncodings中的值
var selectedEncoding = SelectCharacterEncoding(context);
if (selectedEncoding == null)
{
var exception = new UnsupportedContentTypeException(message);
context.ModelState.AddModelError(context.ModelName, exception, context.Metadata);
return InputFormatterResult.FailureAsync();
}
//這裏呼叫了ReadRequestBodyAsync方法
return ReadRequestBodyAsync(context, selectedEncoding);
}
//這就是我們在YamlInputFormatter中實作的ReadRequestBodyAsync方法
publicabstract Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadRequestBodyAsync(
InputFormatterContext context,
Encoding encoding);
protected Encoding? SelectCharacterEncoding(InputFormatterContext context)
{
var requestContentType = context.HttpContext.Request.ContentType;
//解析ContentType
var requestMediaType = string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestContentType) ? default : new MediaType(requestContentType);
if (requestMediaType.Charset.HasValue)
{
var requestEncoding = requestMediaType.Encoding;
if (requestEncoding != null)
{
//在我們設定SupportedEncodings的尋找符合ContentType中包含值的
for (int i = 0; i < SupportedEncodings.Count; i++)
{
if (string.Equals(requestEncoding.WebName, SupportedEncodings[i].WebName, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
return SupportedEncodings[i];
}
}
}
returnnull;
}
return SupportedEncodings[0];
}
}
整體來說
TextInputFormatter
抽象類思路相對清晰,我們實作了
ReadRequestBodyAsync
抽象方法,這個抽象方法被當前類的多載方法
ReadRequestBodyAsync(InputFormatterContext)
方法中呼叫。果然熟悉設計模式之後會發現設計模式無處不在,這裏就是設計模式裏的
樣版方法模式
。好了,我們繼續看源碼
TextInputFormatter
類又繼承了
InputFormatter
抽象類,我們繼續來看它的實作[
點選檢視InputFormatter源碼👈
[2]
]
publicabstract classInputFormatter : IInputFormatter, IApiRequestFormatMetadataProvider
{
//這裏定義了SupportedMediaTypes
public MediaTypeCollection SupportedMediaTypes { get; } = new MediaTypeCollection();
//根據ContentType判斷當前的值是否可以滿足呼叫當前InputFormatter
publicvirtualboolCanRead(InputFormatterContext context)
{
if (SupportedMediaTypes.Count == 0)
{
thrownew InvalidOperationException();
}
if (!CanReadType(context.ModelType))
{
returnfalse;
}
//獲取ContentType的值
var contentType = context.HttpContext.Request.ContentType;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(contentType))
{
returnfalse;
}
//判斷SupportedMediaTypes是否包含ContentType包含的值
return IsSubsetOfAnySupportedContentType(contentType);
}
privateboolIsSubsetOfAnySupportedContentType(string contentType)
{
var parsedContentType = new MediaType(contentType);
//判斷設定的SupportedMediaTypes是否匹配ContentType的值
for (var i = 0; i < SupportedMediaTypes.Count; i++)
{
var supportedMediaType = new MediaType(SupportedMediaTypes[i]);
if (parsedContentType.IsSubsetOf(supportedMediaType))
{
returntrue;
}
}
returnfalse;
}
protectedvirtualboolCanReadType(Type type)
{
returntrue;
}
//核心方法
publicvirtual Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadAsync(InputFormatterContext context)
{
return ReadRequestBodyAsync(context);
}
//抽象方法ReadRequestBodyAsync
publicabstract Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadRequestBodyAsync(InputFormatterContext context);
//獲取當前InputFormatter支持的dContentType
publicvirtual IReadOnlyList<string>? GetSupportedContentTypes(string contentType, Type objectType)
{
if (SupportedMediaTypes.Count == 0)
{
thrownew InvalidOperationException();
}
if (!CanReadType(objectType))
{
returnnull;
}
if (contentType == null)
{
return SupportedMediaTypes;
}
else
{
var parsedContentType = new MediaType(contentType);
List<string>? mediaTypes = null;
foreach (var mediaType in SupportedMediaTypes)
{
var parsedMediaType = new MediaType(mediaType);
if (parsedMediaType.IsSubsetOf(parsedContentType))
{
if (mediaTypes == null)
{
mediaTypes = new List<string>(SupportedMediaTypes.Count);
}
mediaTypes.Add(mediaType);
}
}
return mediaTypes;
}
}
}
這個類比較核心,我們來解析一下裏面設計到的相關邏輯
• 先來看
ReadAsync
方法,這是被呼叫的根入口方法,這個方法呼叫了
ReadRequestBodyAsync
抽象方法,這也是
樣版方法模式
。
ReadRequestBodyAsync
方法正是
TextInputFormatter
類中被實作的。
•
CanRead
方法的功能是根據請求頭裏的
Content-Type
是否可以命中當前
InputFormatter
子類別,所以它是決定我們上面
YamlInputFormatter
方法的校驗方法。
•
GetSupportedContentTypes
方法則是在
Content-Type
裏解析出符合
SupportedMediaTypes
設定的
MediaType
。因為在Http的Header裏,每一個鍵是可以設定多個值的,用
;
分割即可。
上面我們看到了
InputFormatter
類實作了
IInputFormatter
介面,看一下它的定義
publicinterfaceIInputFormatter
{
boolCanRead(InputFormatterContext context);
Task<InputFormatterResult> ReadAsync(InputFormatterContext context);
}
透過
IInputFormatter
介面的定義我們流看到了,它只包含兩個方法
CanRead
和
ReadAsync
。其中
CanRead
方法用來校驗當前請求是否滿足命中
IInputFormatter
實作類,
ReadAsync
方法來執行具體的策略完成請求數據到具體型別的轉換。接下來我們看一下重頭戲,在模型繫結中是如何呼叫
IInputFormatter
介面集合的
public classBodyModelBinderProvider : IModelBinderProvider
{
privatereadonly IList<IInputFormatter> _formatters;
privatereadonly MvcOptions? _options;
public IModelBinder? GetBinder(ModelBinderProviderContext context)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(context);
//判斷當前Action參數是否可以滿足當前模型繫結類
if (context.BindingInfo.BindingSource != null &&
context.BindingInfo.BindingSource.CanAcceptDataFrom(BindingSource.Body))
{
if (_formatters.Count == 0)
{
thrownew InvalidOperationException();
}
var treatEmptyInputAsDefaultValue = CalculateAllowEmptyBody(context.BindingInfo.EmptyBodyBehavior, _options);
returnnew BodyModelBinder(_formatters, _readerFactory, _loggerFactory, _options)
{
AllowEmptyBody = treatEmptyInputAsDefaultValue,
};
}
returnnull;
}
}
透過
BodyModelBinderProvider
類我們可以看到,我們設定的
IInputFormatter
介面的實作類只能滿足繫結
Body
的場景,包含我們上面範例中演示的範例和
[FromBody]
這種形式。接下來我們來看
BodyModelBinder
類中的實作[
點選檢視BodyModelBinder源碼👈
[3]
]
publicpartial classBodyModelBinder : IModelBinder
{
privatereadonly IList<IInputFormatter> _formatters;
privatereadonly Func<Stream, Encoding, TextReader> _readerFactory;
privatereadonly MvcOptions? _options;
publicBodyModelBinder(
IList<IInputFormatter> formatters,
IHttpRequestStreamReaderFactory readerFactory,
MvcOptions? options)
{
_formatters = formatters;
_readerFactory = readerFactory.CreateReader;
_options = options;
}
internalbool AllowEmptyBody { get; set; }
publicasync Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
//獲取Action繫結參數名稱
string modelBindingKey;
if (bindingContext.IsTopLevelObject)
{
modelBindingKey = bindingContext.BinderModelName ?? string.Empty;
}
else
{
modelBindingKey = bindingContext.ModelName;
}
var httpContext = bindingContext.HttpContext;
//組裝InputFormatterContext
var formatterContext = new InputFormatterContext(
httpContext,
modelBindingKey,
bindingContext.ModelState,
bindingContext.ModelMetadata,
_readerFactory,
AllowEmptyBody);
var formatter = (IInputFormatter?)null;
for (var i = 0; i < _formatters.Count; i++)
{
//透過IInputFormatter的CanRead方法來篩選IInputFormatter例項
if (_formatters[i].CanRead(formatterContext))
{
formatter = _formatters[i];
break;
}
}
try
{
//呼叫IInputFormatter的ReadAsync方法,把請求的內容格式轉換成實際的模型物件
var result = await formatter.ReadAsync(formatterContext);
if (result.IsModelSet)
{
//將結果繫結到Action的相關參數上
var model = result.Model;
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(model);
}
}
catch (Exception exception) when (exception is InputFormatterException || ShouldHandleException(formatter))
{
}
}
}
透過閱讀上面的源碼,相信大家已經可以明白了我們定義的
YamlInputFormatter
是如何工作起來的。
YamlInputFormatter
本質是
IInputFormatter
例項。模型繫結類中
BodyModelBinder
呼叫了
ReadAsync
方法本質是呼叫到了
ReadRequestBodyAsync
方法。在這個方法裏我們實作了請求
yml
格式到具體型別物件的轉換,然後把轉換後的物件繫結到了
Action
的參數上。
TextOutputFormatter如何工作
上面我們講解了輸入的格式化轉換程式,知道了
ModelBinding
透過獲取
IInputFormatter
例項來完成請求數據格式到物件的轉換。接下來我們來看一下控制輸出格式的
OutputFormatter
是如何工作的。透過上面自訂的
YamlOutputFormatter
我們可以看到它是繼承自
TextOutputFormatter
抽象類。整體來說它的這個判斷邏輯之類的和
TextInputFormatter
思路整體類似,所以咱們呢大致看一下關於工作過程的源碼即可還是從
WriteResponseBodyAsync
方法入手[
點選檢視TextOutputFormatter源碼👈
[4]
]
publicabstract classTextOutputFormatter : OutputFormatter
{
publicoverride Task WriteAsync(OutputFormatterWriteContext context)
{
//獲取ContentType,需要註意的是這裏並非請求中設定的Content-Type的值,而是程式設定響應頭中的Content-Type值
var selectedMediaType = context.ContentType;
if (!selectedMediaType.HasValue)
{
if (SupportedEncodings.Count > 0)
{
selectedMediaType = new StringSegment(SupportedMediaTypes[0]);
}
else
{
thrownew InvalidOperationException();
}
}
//獲取AcceptCharset的值
var selectedEncoding = SelectCharacterEncoding(context);
if (selectedEncoding != null)
{
var mediaTypeWithCharset = GetMediaTypeWithCharset(selectedMediaType.Value!, selectedEncoding);
selectedMediaType = new StringSegment(mediaTypeWithCharset);
}
else
{
//省略部份程式碼
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
context.ContentType = selectedMediaType;
//寫輸出頭
WriteResponseHeaders(context);
return WriteResponseBodyAsync(context, selectedEncoding);
}
publicabstract Task WriteResponseBodyAsync(OutputFormatterWriteContext context, Encoding selectedEncoding);
}
需要註意的是我們省略了很多源碼,只關註我們關註的地方。這裏沒啥可說的和上面
TextInputFormatter
思路整體類似,也是基於
樣版方法模式
入口方法其實是
WriteAsync
方法。不過這裏需要註意的是在
WriteAsync
方法中
ContentType
,這裏的
ContentType
並非我們在請求時設定的值,而是我們給響應頭中設定值。
TextOutputFormatter
繼承自
OutputFormatter
接下來我們繼續看一下它的實作[
點選檢視OutputFormatter源碼👈
[5]
]
publicabstract classOutputFormatter : IOutputFormatter, IApiResponseTypeMetadataProvider
{
protectedvirtualboolCanWriteType(Type? type)
{
returntrue;
}
//判斷當前請求是否滿足呼叫當前OutputFormatter例項
publicvirtualboolCanWriteResult(OutputFormatterCanWriteContext context)
{
if (SupportedMediaTypes.Count == 0)
{
thrownew InvalidOperationException();
}
//當前Action參數型別是否滿足設定
if (!CanWriteType(context.ObjectType))
{
returnfalse;
}
//這裏的ContentType依然是設定的響應頭而非請求頭
if (!context.ContentType.HasValue)
{
context.ContentType = new StringSegment(SupportedMediaTypes[0]);
returntrue;
}
else
{
//根據設定的輸出頭的ContentType判斷是否滿足自訂時設定的SupportedMediaTypes型別
//比如YamlOutputFormatter中設定的SupportedMediaTypes和設定的響應ContentType是否滿足匹配關系
var parsedContentType = new MediaType(context.ContentType);
for (var i = 0; i < SupportedMediaTypes.Count; i++)
{
var supportedMediaType = new MediaType(SupportedMediaTypes[i]);
if (supportedMediaType.HasWildcard)
{
if (context.ContentTypeIsServerDefined
&& parsedContentType.IsSubsetOf(supportedMediaType))
{
returntrue;
}
}
else
{
if (supportedMediaType.IsSubsetOf(parsedContentType))
{
context.ContentType = new StringSegment(SupportedMediaTypes[i]);
returntrue;
}
}
}
}
returnfalse;
}
//WriteAsync虛方法也就是TextOutputFormatter中從寫的方法
publicvirtual Task WriteAsync(OutputFormatterWriteContext context)
{
WriteResponseHeaders(context);
return WriteResponseBodyAsync(context);
}
publicvirtualvoidWriteResponseHeaders(OutputFormatterWriteContext context)
{
//這裏可以看出寫入的是輸出的ContentType
var response = context.HttpContext.Response;
response.ContentType = context.ContentType.Value ?? string.Empty;
}
}
這裏我們只關註兩個核心方法
CanWriteResult
和
WriteAsync
方法,其中
CanWriteResult
方法判斷當前輸出是否滿足定義的
OutputFormatter
中設定的媒體型別,比如
YamlOutputFormatter
中設定的
SupportedMediaTypes
和設定的響應
ContentType
是否滿足匹配關系,如果顯示的指明了輸出頭是否滿足
text/yaml
或
text/yml
才能執行
YamlOutputFormatter
中的
WriteResponseBodyAsync
方法。一旦滿足
CanWriteResult
方法則會去呼叫
WriteAsync
方法。我們可以看到
OutputFormatter
類實作了
IOutputFormatter
介面,它的定義如下所示
publicinterfaceIOutputFormatter
{
boolCanWriteResult(OutputFormatterCanWriteContext context);
Task WriteAsync(OutputFormatterWriteContext context);
}
一目了然,
IOutputFormatter
介面暴露了
CanWriteResult
和
WriteAsync
兩個能力。咱們上面已經解釋了這兩個方法的用途,在這裏就不再贅述了。我們知道使用
IOutputFormatter
的地方,在
ObjectResultExecutor
類中,
ObjectResultExecutor
類則是在
ObjectResult
類中被呼叫,我們看一下
ObjectResult
呼叫
ObjectResultExecutor
的地方
public classObjectResult : ActionResult, IStatusCodeActionResult
{
publicoverride Task ExecuteResultAsync(ActionContext context)
{
var executor = context.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IActionResultExecutor<ObjectResult>>();
return executor.ExecuteAsync(context, this);
}
}
上面程式碼中獲取的
IActionResultExecutor<ObjectResult>
例項正是
ObjectResultExecutor
例項,這個可以在
MvcCoreServiceCollectionExtensions
類中可以看到[
點選檢視MvcCoreServiceCollectionExtensions源碼👈
[6]
]
services.TryAddSingleton<IActionResultExecutor<ObjectResult>, ObjectResultExecutor>();
好了,回到整體,我們看一下
ObjectResultExecutor
的定義[
點選檢視ObjectResultExecutor源碼👈
[7]
]
publicpartial classObjectResultExecutor : IActionResultExecutor<ObjectResult>
{
publicObjectResultExecutor(OutputFormatterSelector formatterSelector)
{
FormatterSelector = formatterSelector;
}
//ObjectResult方法中呼叫的是該方法
publicvirtual Task ExecuteAsync(ActionContext context, ObjectResult result)
{
var objectType = result.DeclaredType;
//獲取返回物件型別
if (objectType == null || objectType == typeof(object))
{
objectType = result.Value?.GetType();
}
varvalue = result.Value;
return ExecuteAsyncCore(context, result, objectType, value);
}
private Task ExecuteAsyncCore(ActionContext context, ObjectResult result, Type? objectType, object? value)
{
//組裝OutputFormatterWriteContext,objectType為當前返回物件型別,value為返回物件的值
var formatterContext = new OutputFormatterWriteContext(
context.HttpContext,
WriterFactory,
objectType,
value);
//獲取符合當前請求輸出處理常式IOutputFormatter,並傳遞了ObjectResult的ContentTypes值
var selectedFormatter = FormatterSelector.SelectFormatter(
formatterContext,
(IList<IOutputFormatter>)result.Formatters ?? Array.Empty<IOutputFormatter>(),
result.ContentTypes);
//省略部份程式碼
//呼叫IOutputFormatter的WriteAsync的方法
return selectedFormatter.WriteAsync(formatterContext);
}
}
上面的程式碼我們可以看到在
ObjectResultExecutor
類中,透過
OutputFormatterSelector
的
SelectFormatter
方法來選擇使用哪個
IOutputFormatter
例項,需要註意的是呼叫
SelectFormatter
方法的時候傳遞的
ContentTypes
值是來自
ObjectResult
物件的
ContentTypes
內容,也就是我們在設定
ObjectResult
物件的時候可以傳遞的輸出的
Content-Type
值。選擇完成之後在呼叫具體例項的
WriteAsync
方法。我們來看一下
OutputFormatterSelector
實作類的
SelectFormatter
方法如何實作的,在
OutputFormatterSelector
的預設實作類
DefaultOutputFormatterSelector
中[
點選檢視DefaultOutputFormatterSelector源碼👈
[8]
]
publicpartial classDefaultOutputFormatterSelector : OutputFormatterSelector
{
publicoverride IOutputFormatter? SelectFormatter(OutputFormatterCanWriteContext context, IList<IOutputFormatter> formatters, MediaTypeCollection contentTypes)
{
//省略部份程式碼
var request = context.HttpContext.Request;
//獲取請求頭Accept的值
var acceptableMediaTypes = GetAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
var selectFormatterWithoutRegardingAcceptHeader = false;
IOutputFormatter? selectedFormatter = null;
if (acceptableMediaTypes.Count == 0)
{
//如果請求頭Accept沒設定值
selectFormatterWithoutRegardingAcceptHeader = true;
}
else
{
if (contentTypes.Count == 0)
{
//如果ObjectResult沒設定ContentTypes則走這個邏輯
selectedFormatter = SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeaders(
context,
formatters,
acceptableMediaTypes);
}
else
{
//如果ObjectResult設定了ContentTypes則走這個邏輯
selectedFormatter = SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeadersAndContentTypes(
context,
formatters,
acceptableMediaTypes,
contentTypes);
}
//如果透過ObjectResult的ContentTypes沒選擇出來IOutputFormatter這設定該值
if (selectedFormatter == null)
{
if (!_returnHttpNotAcceptable)
{
selectFormatterWithoutRegardingAcceptHeader = true;
}
}
}
if (selectFormatterWithoutRegardingAcceptHeader)
{
if (contentTypes.Count == 0)
{
selectedFormatter = SelectFormatterNotUsingContentType(context, formatters);
}
else
{
selectedFormatter = SelectFormatterUsingAnyAcceptableContentType(context, formatters, contentTypes);
}
}
return selectedFormatter;
}
private List<MediaTypeSegmentWithQuality> GetAcceptableMediaTypes(HttpRequest request)
{
var result = new List<MediaTypeSegmentWithQuality>();
//獲取請求頭裏的Accept的值,因為Accept的值可能有多個,也就是用;分割的情況
AcceptHeaderParser.ParseAcceptHeader(request.Headers.Accept, result);
for (var i = 0; i < result.Count; i++)
{
var mediaType = new MediaType(result[i].MediaType);
if (!_respectBrowserAcceptHeader && mediaType.MatchesAllSubTypes && mediaType.MatchesAllTypes)
{
result.Clear();
return result;
}
}
result.Sort(_sortFunction);
return result;
}
}
上面的
SelectFormatter
方法就是透過各種條件判斷來選擇符合要求的
IOutputFormatter
例項,這裏依次出現了幾個方法,用來可以根據不同條件選擇
IOutputFormatter
,接下來我們根據
出現的順序
來解釋一下這幾個方法的邏輯,首先是
SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeaders
方法
privatestatic IOutputFormatter? SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeaders(
OutputFormatterCanWriteContext formatterContext,
IList<IOutputFormatter> formatters,
IList<MediaTypeSegmentWithQuality> sortedAcceptHeaders)
{
for (var i = 0; i < sortedAcceptHeaders.Count; i++)
{
var mediaType = sortedAcceptHeaders[i];
//把Request的Accept值設定給Response的ContentT-ype
formatterContext.ContentType = mediaType.MediaType;
formatterContext.ContentTypeIsServerDefined = false;
for (var j = 0; j < formatters.Count; j++)
{
var formatter = formatters[j];
if (formatter.CanWriteResult(formatterContext))
{
return formatter;
}
}
}
returnnull;
}
這個方法是透過請求頭的
Accept
值來選擇滿足條件的
IOutputFormatter
例項。還記得上面的
OutputFormatter
類中的
CanWriteResult
方法嗎就是根據
ContentType
判斷是否符合條件,使用的就是這裏的Request的Accept值。第二個出現的選擇方法則是
SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeadersAndContentTypes
方法
privatestatic IOutputFormatter? SelectFormatterUsingSortedAcceptHeadersAndContentTypes(
OutputFormatterCanWriteContext formatterContext,
IList<IOutputFormatter> formatters,
IList<MediaTypeSegmentWithQuality> sortedAcceptableContentTypes,
MediaTypeCollection possibleOutputContentTypes)
{
for (var i = 0; i < sortedAcceptableContentTypes.Count; i++)
{
var acceptableContentType = new MediaType(sortedAcceptableContentTypes[i].MediaType);
for (var j = 0; j < possibleOutputContentTypes.Count; j++)
{
var candidateContentType = new MediaType(possibleOutputContentTypes[j]);
if (candidateContentType.IsSubsetOf(acceptableContentType))
{
for (var k = 0; k < formatters.Count; k++)
{
var formatter = formatters[k];
formatterContext.ContentType = new StringSegment(possibleOutputContentTypes[j]);
formatterContext.ContentTypeIsServerDefined = true;
if (formatter.CanWriteResult(formatterContext))
{
return formatter;
}
}
}
}
}
returnnull;
}
這個方法是透過
ObjectResult
設定了
ContentTypes
去匹配選擇滿足條件請求頭的
Accept
值來選擇
IOutputFormatter
例項。第三個出現的則是
SelectFormatterNotUsingContentType
方法
private IOutputFormatter? SelectFormatterNotUsingContentType(
OutputFormatterCanWriteContext formatterContext,
IList<IOutputFormatter> formatters)
{
foreach (var formatter in formatters)
{
formatterContext.ContentType = new StringSegment();
formatterContext.ContentTypeIsServerDefined = false;
if (formatter.CanWriteResult(formatterContext))
{
return formatter;
}
}
returnnull;
}
這個方法是選擇第一個滿足條件的
IOutputFormatter
例項。還記得上面定義
YamlOutputFormatter
類的時候重寫了
CanWriteResult
方法嗎?就是為了杜絕被預設選中的情況,重寫了
CanWriteResult
方法,裏面添加了驗證邏輯就不會被預設選中。
privatestatic IOutputFormatter? SelectFormatterUsingAnyAcceptableContentType(
OutputFormatterCanWriteContext formatterContext,
IList<IOutputFormatter> formatters,
MediaTypeCollection acceptableContentTypes)
{
foreach (var formatter in formatters)
{
foreach (var contentType in acceptableContentTypes)
{
formatterContext.ContentType = new StringSegment(contentType);
formatterContext.ContentTypeIsServerDefined = true;
if (formatter.CanWriteResult(formatterContext))
{
return formatter;
}
}
}
returnnull;
}
這個方法說的比較簡單,就是透過
ObjectResult
設定了
ContentTypes
去匹配選擇滿足條件的
IOutputFormatter
例項。
到這裏相信大家對關於
TextOutputFormatter
是如何工作的有了大致的了解,本質就是在
ObjectResultExecutor
類中選擇合適的滿足條件的
IOutputFormatter
例項。我們在
Action
中返回
POCO
物件、
ActionResult<Type>
、
OkObjectResult
等本質都是返回的
ObjectResult
型別。
小結
相信透過這一小節對
TextInputFormatter
和
TextOutputFormatter
源碼的分析,和它們是如何工作的進行了大致的講解。其實如果理解了源碼,總結起來也很簡單
• 模型繫結類中
BodyModelBinder
呼叫了
InputFormatter
例項來進行對指定請求的內容進行格式轉換,繫結到模型參數上的,
•
ObjectResult
類的執行類
ObjectResultExecutor
類中透過呼叫滿足條件
OutputFormatter
例項,來決定把模型輸出成那種型別的數據格式,但是需要註意重寫
CanWriteResult
方法防止被作為預設程式輸出。
控制了模型繫結和輸出物件轉換,我們也就可以直接控制請求數據和輸出數據的格式控制了。當然想更好的了解更多的細節,解惑心中疑問,還是得閱讀和偵錯具體的源碼。
相關資料
由於文章中涉及到的源碼都是關於格式化程式工作過程中涉及到的源碼,其它的相關源碼和地址我們並沒有展示出來,這裏我將羅列一下對該功能理解有幫助的相關地址,方便大家閱讀
• Custom formatters in ASP.NET Core Web API [9]
• 內建的SystemTextJson格式化程式相關
• MvcCoreMvcOptionsSetup [10]
• SystemTextJsonInputFormatter [11]
• SystemTextJsonOutputFormatter [12]
• 內建的Xml格式化程式相關
• XmlSerializerMvcOptionsSetup [13]
• XmlSerializerInputFormatter [14]
• XmlSerializerOutputFormatter [15]
• ActionResultOfT.Convert()方法 [16]
• ActionResultTypeMapper [17]
• SyncObjectResultExecutor [18]
• FormatFilter [19]
總結
本篇文章我們透過演示範例和講解源碼的方式了解了
ASP.NET Core WebAPI
中的格式化程式,知道結構的話了解它其實並不難,只是其中的細節比較多,需要慢慢梳理。涉及到的源碼比較多,可以把本文當做一個簡單的教程來看。寫文章既是把自己對事物的看法分享出來,也是把自己的感悟記錄下來方便翻閱。我個人很喜歡閱讀源碼,透過開始閱讀源碼感覺自己的水平有了很大的提升,閱讀源碼與其說是一個行為不如說是一種意識。明顯的好處,一個是為了讓自己對這些理解更透徹,閱讀過程中可以引發很多的思考。二是透過源碼可以解決很多實際的問題,畢竟大家都這麽說源碼之下無秘密。
參照連結
[1]
點選檢視TextInputFormatter源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/TextInputFormatter.cs#L60
[2]
點選檢視InputFormatter源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/InputFormatter.cs
[3]
點選檢視BodyModelBinder源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/ModelBinding/Binders/BodyModelBinder.cs
[4]
點選檢視TextOutputFormatter源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/TextOutputFormatter.cs#L168
[5]
點選檢視OutputFormatter源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/OutputFormatter.cs#L157
[6]
點選檢視MvcCoreServiceCollectionExtensions源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/DependencyInjection/MvcCoreServiceCollectionExtensions.cs#L235
[7]
點選檢視ObjectResultExecutor源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Infrastructure/ObjectResultExecutor.cs
[8]
點選檢視DefaultOutputFormatterSelector源碼👈:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Infrastructure/DefaultOutputFormatterSelector.cs#L50
[9]
Custom formatters in ASP.NET Core Web API:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/web-api/advanced/custom-formatters?view=aspnetcore-8.0
[10]
MvcCoreMvcOptionsSetup:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Infrastructure/MvcCoreMvcOptionsSetup.cs
[11]
SystemTextJsonInputFormatter:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/SystemTextJsonInputFormatter.cs
[12]
SystemTextJsonOutputFormatter:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/SystemTextJsonOutputFormatter.cs
[13]
XmlSerializerMvcOptionsSetup:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Formatters.Xml/src/DependencyInjection/XmlSerializerMvcOptionsSetup.cs
[14]
XmlSerializerInputFormatter:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Formatters.Xml/src/XmlSerializerInputFormatter.cs
[15]
XmlSerializerOutputFormatter:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Formatters.Xml/src/XmlSerializerOutputFormatter.cs
[16]
ActionResultOfT.Convert()方法:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/ActionResultOfT.cs#L78
[17]
ActionResultTypeMapper:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Infrastructure/ActionResultTypeMapper.cs
[18]
SyncObjectResultExecutor:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Infrastructure/ActionMethodExecutor.cs#L156
[19]
FormatFilter:
https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/v8.0.2/src/Mvc/Mvc.Core/src/Formatters/FormatFilter.cs











