前言
大多數程式設計師在平時工作中,都是增刪改查。這裏我跟大家講解如何利用 CompletableFuture 最佳化計畫程式碼,使計畫效能更佳!
為什麽要用異步編程
舉個例子:使用者登入成功,需要返回前端使用者角色,選單許可權,個人資訊,使用者余額,積分情況等。正常邏輯是依次查詢不同表,得到對應的數據封裝返回給前端,程式碼如下:
@Test
public void login(Long userId){
log.info("開始查詢使用者全部資訊---序列!");
// 查詢使用者角色資訊
getUserRole(userId);
// 查詢使用者選單資訊
getUserMenu(userId);
// 查詢使用者余額資訊
getUserAmount(userId);
// 查詢使用者積分資訊
getUserIntegral(userId);
log.info("封裝使用者資訊返回給前端!");
}
假如查詢使用者角色,使用者選單,使用者余額,使用者積分分別耗時500,200,200,100毫秒,則登入介面耗時為1秒。如果采用異步(多執行緒並列)形式,則登入介面耗時以單個查詢最慢的任務為主,為查詢使用者角色資訊500毫秒。相當於登入介面效能提升一倍!查詢任務越多,則其效能提升越大!
程式碼演示(序列):
@Test
public void login() throws InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("開始查詢使用者全部資訊!");
log.info("開始查詢使用者角色資訊!");
Thread.sleep(500);
String role = "管理員";
log.info("開始查詢使用者選單資訊!");
Thread.sleep(200);
String menu = "首頁,帳戶管理,積分管理";
log.info("開始查詢查詢使用者余額資訊!");
Thread.sleep(200);
Integer amount = 1999;
log.info("開始查詢查詢查詢使用者積分資訊!");
Thread.sleep(100);
Integer integral = 1015;
log.info("封裝使用者資訊返回給前端!");
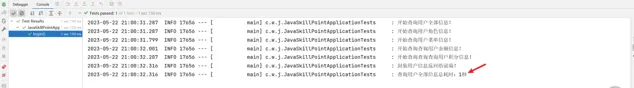
log.info("查詢使用者全部資訊總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
結果:
程式碼演示(異步):
@Test
public void asyncLogin() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("開始查詢使用者角色資訊!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("role", "管理員");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢使用者角色資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return roleMap;
});
log.info("開始查詢使用者選單資訊!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> menuFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> menuMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
menuMap.put("menu", "首頁,帳戶管理,積分管理");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢使用者選單資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return menuMap;
});
log.info("開始查詢使用者余額資訊!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 1999);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢使用者余額資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return amountMap;
});
log.info("開始查詢使用者積分資訊!");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> integralFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> integralMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
integralMap.put("integral", 1015);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢使用者積分資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
return integralMap;
});
roleFuture.join();
menuFuture.join();
amountFuture.join();
integralFuture.join();
log.info("查詢使用者全部資訊總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "毫秒");
}
結果:
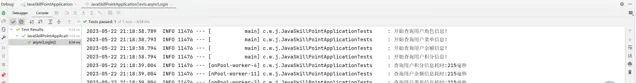
直觀的可以看出,異步執行的優勢!
回顧Future
Future是什麽?
Java 1.5中引入Callable解決多執行緒執行無返回值的問題。
Future是為了配合Callable/Runnable而產生的。簡單來講,我們可以透過future來對任務查詢、取消、執行結果的獲取,是呼叫方與異步執行方之間溝通的橋梁。
FutureTask 實作了RunnableFuture介面,同時具有Runnable、Future的能力,即既可以作為Future得到Callable的返回值,又可以作為一個Runnable。
CompletableFuture實作了Futrue介面。
Future是Java5新加的一個介面,它提供了一種異步平行計算的功能。如果主執行緒需要執行一個很耗時的計算任務,我們可以將這個任務透過Future放到異步執行緒中去執行。主執行緒繼續處理其他任務,處理完成後,再透過Future獲取計算結果。
Future可以在連續流程中滿足數據驅動的並行需求,既獲得了並行執行的效能提升,又不失連續流程的簡潔優雅。
程式碼演示(不使用自訂執行緒池):
@Test
public void callable() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Callable amountCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(6000);
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢金額資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}
};
FutureTask<Map> amountFuture = new FutureTask<>(amountCall);
new Thread(amountFuture).start();
Callable roleCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Map<String, String> roleMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理員");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢角色資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return roleMap;
}
};
FutureTask<Map> roleFuture = new FutureTask<>(roleCall);
new Thread(roleFuture).start();
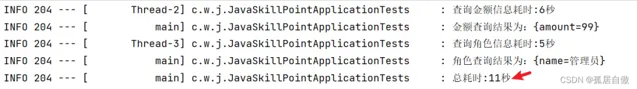
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountFuture.get());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleFuture.get());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("總耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}

「
這裏要註意:Future對於結果的獲取,不是很友好,只能透過阻塞或者輪詢的方式得到任務的結果。
Future.get()
就是阻塞呼叫,線上程獲取結果之前get方法會一直阻塞;Future提供了一個isDone方法,可以在程式中輪詢這個方法查詢執行結果。
這裏的
amountFuture.get()
如果放到如下圖所示的位置,則amountFuture下面的執行緒將等
amountFuture.get()
完成後才能執行,沒有執行完,則一直阻塞。

結果:
程式碼演示(使用自訂執行緒池):
@Test
public void executor() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Callable amountCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(6000);
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢金額資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}
};
Callable roleCall = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Map<String, String> roleMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理員");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢使用者角色資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return roleMap;
}
};
Future amountFuture = executor.submit(amountCall);
Future roleFuture = executor.submit(roleCall);
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountFuture.get());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleFuture.get());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("總耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
結果:

CompletableFuture使用場景
建立異步任務
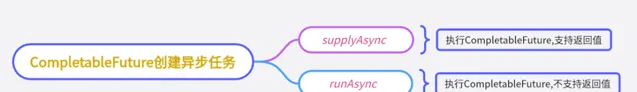
CompletableFuture建立異步任務,一般有supplyAsync和runAsync兩個方法:
supplyAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,支持返回值。
runAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,沒有返回值。
supplyAsync方法
//使用預設內建執行緒池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據supplier構建執行任務
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//自訂執行緒,根據supplier構建執行任務
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
runAsync方法
//使用預設內建執行緒池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據runnable構建執行任務
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自訂執行緒,根據runnable構建執行任務
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
程式碼演示:
@Test
// supplyAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,支持返回值
public void defaultSupplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 構建執行任務
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢金額資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
// 這行程式碼在這裏 則會進行6秒的阻塞 下面程式碼其他執行緒無法建立
// 只能等這個執行緒6秒過後結束才能建立其他執行緒
// Map<String, Object> userMap = userCompletableFuture.get();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理員");
return roleMap;
});
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// supplyAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,支持返回值
public void customSupplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 自訂執行緒池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 99);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("查詢金額資訊耗時:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
}, executorService);
// 這行程式碼在這裏 則會進行6秒的阻塞 下面程式碼其他執行緒無法建立
// 只能等這個執行緒6秒過後結束才能建立其他執行緒
// Map<String, Object> userMap = userCompletableFuture.get();
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> roleMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
roleMap.put("name", "管理員");
return roleMap;
}, executorService);
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
// 執行緒池需要關閉
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// runAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,沒有返回值
public void defaultRunAsync() {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行金額增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行角色增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
@Test
// runAsync執行CompletableFuture任務,沒有返回值
public void customRunAsync() {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行金額增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> roleCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行角色增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}, executor);
log.info("金額查詢結果為:" + amountCompletableFuture.join());
log.info("角色查詢結果為:" + roleCompletableFuture.join());
// 關閉執行緒池
executor.shutdown();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
註意:這裏的get()與join()都是獲取任務執行緒的返回值。join()方法丟擲的是uncheck異常(即RuntimeException),不會強制開發者丟擲, 會將異常包裝成
CompletionException
異常 /
CancellationException
異常,但是本質原因還是程式碼記憶體在的真正的異常;
get()方法丟擲的是經過檢查的異常,
ExecutionException
,
InterruptedException
需要使用者手動處理(丟擲或者 try catch)。
異步任務回呼
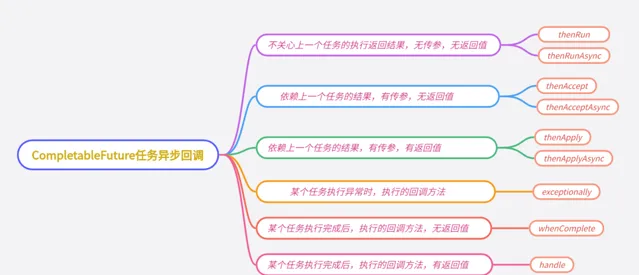
thenRun / thenRunAsync
CompletableFuture的thenRun方法,通俗點講就是,做完第一個任務後,再做第二個任務。某個任務執行完成後,執行回呼方法;但是前後兩個任務沒有參數傳遞,第二個任務也沒有返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
thenRun / thenRunAsync的區別? 源碼解釋:
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
如果你執行第一個任務的時候,傳入了一個自訂執行緒池:
呼叫thenRun方法執行第二個任務時,則第二個任務和第一個任務是共用同一個執行緒池。
呼叫thenRunAsync執行第二個任務時,則第一個任務使用的是你自己傳入的執行緒池,第二個任務使用的是ForkJoin執行緒池。
後面介紹的thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它們之間的區別也是這個哈!
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 執行第一個任務後 可以繼續執行第二個任務 兩個任務之間無傳參 無返回值
public void defaultThenRun() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Void> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行金額增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenRun(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("執行角色增刪改操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
});
thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
結果:
thenAccept / thenAcceptAsync
CompletableFuture的thenAccept方法表示,第一個任務執行完成後,執行第二個回呼方法任務,會將該任務的執行結果,作為入參,傳遞到回呼方法中,但是回呼方法是沒有返回值的。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 執行第一個任務後 可以繼續執行第二個任務 並攜帶第一個任務的返回值 第二個任務執行完沒有返回值
public void defaultThenAccept() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("執行金額查詢操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenAccept((map) -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 90) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("金額充足,可以購買!:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
} else {
log.info("金額不足,無法購買!:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
});
thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
結果:
thenApply / thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture的thenApply方法表示,第一個任務執行完成後,執行第二個回呼方法任務,會將該任務的執行結果,作為入參,傳遞到回呼方法中,並且回呼方法是有返回值的。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 執行第一個任務後 可以繼續執行第二個任務 並攜帶第一個任務的返回值 第二個任務執行完有返回值
public void defaultThenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("執行金額查詢操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenApply((map) -> {
int number = 0;
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 可口可樂3元一瓶 看金額一共能購買多少瓶
number = Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) / 3;
}
return number;
});
log.info("當前金額一共可以買" + thenCompletableFuture.get() + "瓶可口可樂!");
Integer integer = thenCompletableFuture.get();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
結果:
exceptionally
CompletableFuture的exceptionally方法表示,某個任務執行異常時,執行的回呼方法;並且有丟擲異常作為參數,傳遞到回呼方法。
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(
Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) {
return uniExceptionallyStage(fn);
}
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 某個任務執行異常時,執行的回呼方法;並且有丟擲異常作為參數,傳遞到回呼方法。
public void exceptionally() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long lordStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Map> amountCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Map<String, Object> amountMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
amountMap.put("amount", 90);
log.info("執行金額查詢操作用時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + "秒");
return amountMap;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCompletableFuture = amountCompletableFuture.thenApply((map) -> {
int number = 0;
if (Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) > 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 可口可樂3元一瓶 看金額一共能購買多少瓶
number = Integer.parseInt(map.get("amount").toString()) / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new ArithmeticException(); // 這裏一定要將異常拋除了,不然exceptionally無效
}
}
return number;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> exceptionFuture = thenCompletableFuture.exceptionally((e) -> {
log.error("除數為0,則預設商為0!");
return 0;
});
log.info("當前金額一共可以買" + thenCompletableFuture.get() + "瓶可口可樂!");
exceptionFuture.get();
log.info("總耗時:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lordStartTime) / 1000 + "秒");
}
「
註意:這裏的異常一定要丟擲來,不然exceptionally無效!
whenComplete
CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某個任務執行完成後,執行的回呼方法,無返回值;並且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上個任務的結果。
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {
return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 某個任務執行完成後,執行的回呼方法,無返回值;並且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上個任務的結果。
public void whenComplete() {
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return"周杰倫";
});
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture1 = stringCompletableFuture.whenComplete((a, throwable) -> {
log.info("周杰倫喜歡唱");
});
log.info("輸出結果為第一個任務:" + stringCompletableFuture1.join());
}
結果:
handle
CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某個QQ帳號買號平台地圖任務執行完成後,執行回呼方法,並且是有返回值的;並且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回呼方法執行的結果。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(
BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {
return uniHandleStage(null, fn);
}
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 某個任務執行完成後,執行的回呼方法,有返回值;並且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是第二個任務的結果。
public void handle() {
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return"周杰倫";
});
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture1 = stringCompletableFuture.handle((a, throwable) -> {
return"周杰倫喜歡唱歌!";
});
log.info("輸出結果為第二個任務:" + stringCompletableFuture1.join());
}
結果:
多個任務組合處理
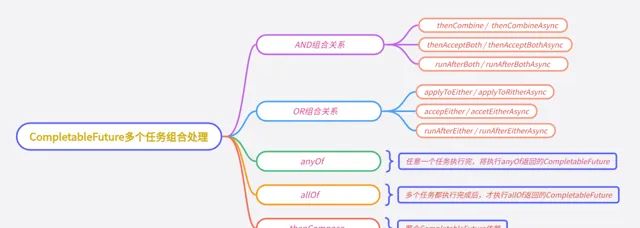
AND組合關系
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth都表示:將兩個CompletableFuture組合起來,只有這兩個都正常執行完了,才會執行某個任務。
thenCombine:會將兩個任務的執行結果作為方法入參,傳遞到指定方法中,且有返回值。
thenAcceptBoth: 會將兩個任務的執行結果作為方法入參,傳遞到指定方法中,且無返回值。
runAfterBoth 不會把執行結果當做方法入參,且沒有返回值。
程式碼演示:
@Test
public void thenCombine() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 7;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 2).thenCombine(first, Integer::sum);
log.info("結果為:" + second.join());
}
結果為:
OR組合關系
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 都表示:將兩個CompletableFuture組合起來,只要其中一個執行完了,就會執行某個任務。
applyToEither:會將已經執行完成的任務,作為方法入參,傳遞到指定方法中,且有返回值。
acceptEither: 會將已經執行完成的任務,作為方法入參,傳遞到指定方法中,且無返回值。
runAfterEither:不會把執行結果當做方法入參,且沒有返回值。
程式碼演示:
@Test
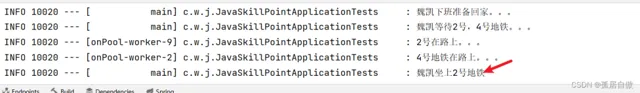
public void applyToEither1() {
log.info("魏凱下班準備回家。。。");
log.info("魏凱等待2號,4號地鐵。。。");
CompletableFuture<String> busCF = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("2號在路上。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"2";
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("4號地鐵在路上。。。");
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"4";
}), first -> first + "號");
log.info("魏凱坐上" + busCF.join() + "地鐵");
}
@Test
// OR
public void applyToEither() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 7;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 7;
}).applyToEither(first, num -> num);
log.info("最後結果為:" + second.join());
}
結果演示:
AllOf
所有任務都執行完成後,才執行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一個任務異常,allOf的CompletableFuture,執行get方法,會丟擲異常。
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 所有任務都執行完成後,才執行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一個任務異常,allOf的CompletableFuture,執行get方法,會丟擲異常。
// 這裏第一次執行沒有睡眠的話,是可以直接執行第三個任務的。如果有睡眠,則需要手動join啟動。
public void allOf() {
CompletableFuture<Void> first = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(2000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
log.info("第一個任務執行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> second = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(500);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
log.info("第二個任務執行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(first, second).whenComplete((m, n) -> {
log.info("第三個任務完成!");
});
// voidCompletableFuture.join();
}
結果:
「
註意:這裏第一次啟動執行沒有睡眠的話,是可以直接執行第三個任務的,因為這兩個任務都執行完成,啟動的瞬間第三個也同時執行完。如果有睡眠,則需要手動join啟動,等待最長睡眠任務時間過後,第三個任務完成!
AnyOf
任意一個任務執行完,就執行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果執行的任務異常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,執行get方法,會丟擲異常。
程式碼演示:
@Test
// 前提任務任意執行完一個,則目標任務執行。其他前提任務則不在執行。
// 任意一個任務執行完,就執行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果執行的任務異常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,執行get方法,會丟擲異常。
public void anyOf() {
CompletableFuture<Void> first = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("第一個任務執行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> second = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("第二個任務執行完成!");
});
CompletableFuture<Object> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(first, second).whenComplete((m, n) -> {
log.info("第三個任務完成!");
});
voidCompletableFuture.join();
}
結果:
thenCompose
thenCompose方法會在某個任務執行完成後,將該任務的執行結果,作為方法入參,去執行指定的方法。該方法會返回一個新的CompletableFuture例項。
如果該CompletableFuture例項的result不為null,則返回一個基於該result新的CompletableFuture例項。
如果該CompletableFuture例項為null,然後就執行這個新任務。
程式碼演示:
@Test
public void thenCompose1() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 4)
.thenCompose(value -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// thenCompose方法返回一個新的CompletableFuture
if (Integer.valueOf(4).equals(value)) {
return 66;
} else {
return 99;
}
}));
log.info("結果:" + stringCompletableFuture.join());
}
@Test
public void thenCompose() {
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("第一個任務");
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 4)
.thenCompose((data) -> {
log.info("data為:" + data);
return first;
});
log.info("結果:" + stringCompletableFuture.join());
}
結果:
CompletableFuture註意點
Future需要獲取返回值,才能獲取異常資訊
@Test
public void futureTest(){
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Integer> integerCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int m = 9;
int n = 0;
return m / n;
},executor);
// integerCompletableFuture.join(); // 這行程式碼不加,則不會丟擲異常
}
Future需要獲取返回值,才能獲取到異常資訊。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到異常資訊。小夥伴們使用的時候,註意一下哈,考慮是否加try…catch…或者使用exceptionally方法。
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的
//反例
CompletableFuture.get();
//正例
CompletableFuture.get(9, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它來獲取異步呼叫的返回值,需要添加超時時間
預設執行緒池的註意點
CompletableFuture程式碼中又使用了預設的執行緒池,處理的執行緒個數是電腦CPU核數-1。在大量請求過來的時候,處理邏輯復雜的話,響應會很慢。一般建議使用自訂執行緒池,最佳化執行緒池配置參數。
自訂執行緒池時,註意飽和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我們一般建議使用
future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
。並且一般建議使用自訂執行緒池。但是如果執行緒池拒絕策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,當執行緒池飽和時,會直接丟棄任務,不會拋棄異常。
因此建議,CompletableFuture執行緒池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然後耗時的異步執行緒,做好執行緒池隔離!
<END>











