
概述: 早在 2005 年,随着 C# 2.0 标准的发布,我们可以通过从当前上下文中捕获变量来将变量传递给匿名委托的正文。2008 年,C# 3.0 为我们带来了 lambda、用户匿名类、LINQ 请求等等。现在是 2017 年 1 月,大多数 C# 开发人员都期待着 C# 7.0 标准的发布,它应该为我们提供一系列新的有用功能。但是,仍有一些旧功能需要修复。这就是为什么有很多方法可以搬起石头砸自己的脚。今天我们将讨论其中之一,它与 C# 中匿名函数主体中一个非常不明显的变量捕获机制有关。介绍正如我上面所说,我们将讨论 C# 中匿名函数主体中变量捕获机制的特殊性。我应该提前警告一下,这篇文章将包含
早在 2005 年,随着 C# 2.0 标准的发布,我们可以通过从当前上下文中捕获变量来将变量传递给匿名委托的正文。2008 年,C# 3.0 为我们带来了 lambda、用户匿名类、LINQ 请求等等。现在是 2017 年 1 月,大多数 C# 开发人员都期待着 C# 7.0 标准的发布,它应该为我们提供一系列新的有用功能。但是,仍有一些旧功能需要修复。这就是为什么有很多方法可以搬起石头砸自己的脚。今天我们将讨论其中之一,它与 C# 中匿名函数主体中一个非常不明显的变量捕获机制有关。
介绍
正如我上面所说,我们将讨论 C# 中匿名函数主体中变量捕获机制的特殊性。我应该提前警告一下,这篇文章将包含大量的技术细节,但我希望有经验的程序员和初学者都会发现我的文章有趣且易于理解。
但说得够多了。我将给你一个简单的代码示例,你应该告诉,控制台中将打印什么。
所以,我们开始吧。
voidFoo()
{
var actions = newList<Action>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
actions.Add(() => Console.WriteLine(i));
}
foreach(var a in actions)
{
a();
}
}
现在请注意,这是答案。控制台将打印数字 10 十次。
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
这篇文章是为那些不这么认为的人准备的。让我们试着梳理一下,这种行为的原因是什么。
为什么会这样?
在类中声明匿名函数(可以是匿名委托或 lambda)后,将在编译期间声明另一个容器类,该类包含所有捕获变量的字段和一个包含匿名函数主体的方法。上面给出的代码片段的程序的反汇编结构如下:
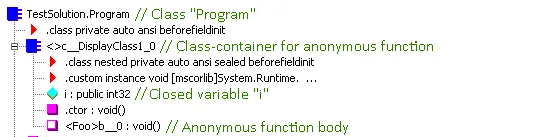
在本例中,此片段中的 Foo 方法在 Program 类中声明。编译器为 lambda ( ) => Console.WriteLine( i) 生成了一个容器类_c__Display class1_0 ,并在类容器内部生成了一个字段 i ,该字段具有一个具有相同名称和方法 b__0 的捕获变量 ,_其中包含 lambda 的主体。
让我们考虑一下 b__0 方法(lambda 正文)的反汇编 IL 代码以及我的评论:
.method assembly hidebysig instance void '<Foo>b__0'() cil managed
{
.maxstack 8
// Puts the current class item (equivalent to 'this')
// to the top of the stack.
// It is necessary for the access to
// the fields of the current class.
IL_0000: ldarg.0
// Puts the value of the 'i' field to the top of the stack
// of the current class instance
IL_0001: ldfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::i
// Calls a method to output the string to the console.
// Passes values from the stack as arguments.
IL_0006: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(int32)
// Exits the method.
IL_000b: ret
}
没错,这正是我们在 lambda 中所做的,没有魔法。让我们继续。
众所周知,int 类型(全称 Int32)是一个结构体,这意味着它通过值传递,而不是通过引用传递。
在创建容器类实例期间,应复制 i 变量的值(根据逻辑)。如果您错误地回答了我在文章开头的问题,那么您很可能期望容器将在代码中声明 lambda 之前创建。
实际上,在 Foo 方法中编译后根本不会创建 i 变量。取而代之的是,将创建容器类 c__Display class1_0 的实例,并且其字段将使用 0 而不是 i 变量进行初始化。此外,在我们使用局部变量 i 的所有片段中,都会有一个使用容器类的字段。
重要的一点是,容器类的实例是在循环之前创建的,因为它的字段 i 将在循环中用作迭代器。
因此,我们为 for 循环的所有迭代获得一个容器类的实例。在每次迭代时向_操作_列表添加一个新的 lambda,我们实际上添加了对之前创建的容器类实例的相同引用。因此,当我们使用 foreach 循环遍历_操作_列表的所有项时,它们都具有相同的容器类实例。我们考虑到 for 循环在每次迭代后(甚至在最后一次迭代之后)递增迭代器的值,那么在执行 for 循环后,退出循环后容器类内 i 字段的值等于 10。
您可以通过查看 Foo 方法的反汇编 IL 代码来确保它(带有我的评论):
.method private hidebysig instance voidFoo() cil managed
{
.maxstack 3
// -========== DECLARATION OF LOCAL VARIABLES ==========-
.localsinit(
// A list of 'actions'.
[0] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1
< class [mscorlib]System.Action> actions,
// A container class for the lambda.
[1] classTestSolution.Program/
'<>c__Display class1_0' 'CS$<>8__locals0',
// A technical variable V_2 is necessary for temporary
// storing the results of the addition operation.
[2] int32 V_2,
// Technical variable V_3 is necessary for storing
// the enumerator of the 'actions' list during
// the iteration of the 'foreach' loop.
[3] valuetype
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1/Enumerator< class
[mscorlib]System.Action> V_3)
// -================= INITIALIZATION =================-
// An instance of the Actions list is created and assigned to the
// 'actions' variable.
IL_0000: newobj instance void class
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::.ctor()
IL_0005: stloc.0
// An instance of the container class is created
// and assigned to a corresponding local variable
IL_0006: newobj instance void
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::.ctor()
IL_000b: stloc.1
// A reference of the container class is loaded to the stack.
IL_000c: ldloc.1
// Number 0 is loaded to the stack.
IL_000d: ldc.i4.0
// 0 is assigned to the 'i' field of the previous
// object on the stack (an instance of a container class).
IL_000e: stfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::i
// -================= THE FOR LOOP =================-
// Jumps to the command IL_0037.
IL_0013: br.s IL_0037
// The references of the 'actions'
// list and an instance of the container class
// are loaded to the stack.
IL_0015: ldloc.0
IL_0016: ldloc.1
// The reference to the 'Foo' method of the container class
// is loaded to the stack.
IL_0017: ldftn instance void
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::'<Foo>b__0'()
// An instance of the 'Action' class is created and the reference
// to the 'Foo' method of the container class is passed into it.
IL_001d: newobj instance void
[mscorlib]System.Action::.ctor(object, native int)
// The method 'Add' is called for the 'actions' list
// by adding an instance of the 'Action' class.
IL_0022: callvirt instance void class
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::Add(!0)
// The value of the 'i' field of the instance of a container class
// is loaded to the stack.
IL_0027: ldloc.1
IL_0028: ldfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::i
// The value of the 'i' field is assigned
// to the technical variable 'V_2'.
IL_002d: stloc.2
// The reference to the instance of a container class and the value
// of a technical variable 'V_2' is loaded to the stack.
IL_002e: ldloc.1
IL_002f: ldloc.2
// 1 is loaded to the stack.
IL_0030: ldc.i4.1
// It adds two first values on the stack
// and assigns them to the third.
IL_0031: add
// The result of the addition is assigned to the 'i' field
// (in fact, it is an increment)
IL_0032: stfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::i
// The value of the 'i' field of the container class instance
// is loaded to the stack.
IL_0037: ldloc.1
IL_0038: ldfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::i
// 10 is loaded to the stack.
IL_003d: ldc.i4.s 10
// If the value of the 'i' field is less than 10,
// it jumps to the command IL_0015.
IL_003f: blt.s IL_0015
// -================= THE FOREACH LOOP =================-
//// The reference to the 'actions' list is loaded to the stack.
IL_0041: ldloc.0
// The technical variable V_3 is assigned with the result
// of the 'GetEnumerator' method of the 'actions' list.
IL_0042: callvirt instance valuetype
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1/Enumerator<!0> class
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::GetEnumerator()
IL_0047: stloc.3
// The initialization of the try block
// (the foreach loop is converted to
// the try-finally construct)
.try
{
// Jumps to the command IL_0056.
IL_0048: br.s IL_0056
// Calls get_Current method of the V_3 variable.
// The result is written to the stack.
// (A reference to the Action object in the current iteration).
IL_004a: ldloca.s V_3
IL_004c: call instance !0 valuetype
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1/Enumerator< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::get_Current()
// Calls the Invoke method of the Action
// object in the current iteration
IL_0051: callvirt instance void
[mscorlib]System.Action::Invoke()
// Calls MoveNext method of the V_3 variable.
// The result is written to the stack.
IL_0056: ldloca.s V_3
IL_0058: call instance bool valuetype
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1/Enumerator< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::MoveNext()
// If the result of the MoveNext method is not null,
// then it jumps to the IL_004a command.
IL_005d: brtrue.s IL_004a
// Finishes the try block execution and jumps to finally.
IL_005f: leave.s IL_006f
} // end .try
finally
{
// Calls the Dispose method of the V_3 variable.
IL_0061: ldloca.s V_3
IL_0063: constrained. Valuetype
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1/Enumerator< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>
IL_0069: callvirt instance void
[mscorlib]System.IDisposable::Dispose()
// Finishes the execution of the finally block.
IL_006e: endfinally
}
// Finishes the execution of the current method.
IL_006f: ret
}
结论
Microsoft 的人说这是一个功能,而不是一个错误,这种行为是故意的,旨在提高程序的性能。您将通过此链接找到更多信息。实际上,它会导致新手开发人员的错误和困惑。
一个有趣的事实是, foreach 循环在 C# 5.0 标准之前具有相同的行为。Microsoft 被关于错误跟踪器中非直观行为的抱怨轰炸,但随着 C# 5.0 标准的发布,通过在每个循环迭代中声明迭代器变量来改变这种行为,而不是在编译阶段之前,但对于所有其他结构,类似的行为保持不变。有关详细信息,请参阅_「中断性变更_」部分中的链接。
你可能会问如何避免这样的错误?其实答案很简单。您需要跟踪捕获的位置和变量。请记住,容器类将在您声明要捕获的变量的位置创建。如果捕获发生在循环的主体中,并且变量是在循环外部声明的,则有必要在循环主体内将其重新分配给新的局部变量。开头给出的示例的正确版本可以如下所示:
voidFoo()
{
var actions = newList<Action>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
var index = i; // <=
actions.Add(() => Console.WriteLine(index));
}
foreach(var a in actions)
{
a();
}
}
如果执行此代码,控制台将显示从 0 到 9 的数字,如预期所示:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
从此示例中查看 for 循环的 IL 代码,我们将看到在循环的每次迭代中都会创建一个容器类的实例。因此,操作列表将包含对具有正确迭代器值的各种实例的引用。
// -================= THE FOR LOOP =================-
// Jumps to the command IL_002d.
IL_0008: br.s IL_002d
// Creates an instance of a container class
// and loads the reference to the stack.
IL_000a: newobj instance void
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::.ctor()
IL_000f: stloc.2
IL_0010: ldloc.2
// Assigns the 'index' field in the container class
// with a value 'i'.
IL_0011: ldloc.1
IL_0012: stfld int32
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::index
// Creates an instance of the 'Action' class with a reference to
// the method of a container class and add it to the 'actions' list.
IL_0017: ldloc.0
IL_0018: ldloc.2
IL_0019: ldftn instance void
TestSolution.Program/'<>c__Display class1_0'::'<Foo>b__0'()
IL_001f: newobj instance void
[mscorlib]System.Action::.ctor(object, native int)
IL_0024: callvirt instance void class
[mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List'1< class
[mscorlib]System.Action>::Add(!0)
// Performs the increment to the 'i' variable
IL_0029: ldloc.1
IL_002a: ldc.i4.1
IL_002b: add
IL_002c: stloc.1
// Loads the value of the 'i' variable to the stack
// This time it is not in the container class
IL_002d: ldloc.1
// Compares the value of the variable 'i' with 10.
// If 'i < 10', then jumps to the command IL_000a.
IL_002e: ldc.i4.s 10
IL_0030: blt.s IL_000a
最后,让我提醒您,我们都是人类,我们都会犯错误,这就是为什么在寻找错误和错别字时只希望人为因素是不合逻辑的,并且通常是漫长且资源密集型的。因此,使用技术解决方案来检测代码中的错误始终是一个好主意。机器不会感到疲倦,并且完成工作的速度要快得多。
如果你喜欢我的文章,请给我一个赞!谢谢










