点击上方 "
Python人工智能技术
"
关注,
星标或者置顶
22点24分准时推送,第一时间送达
后台回复「
大礼包
」,送你特别福利
编辑:乐乐 | 来自:https://www.cnblogs.com/sbhglqy/p/18163862
上一篇:
正文
大家好,我是Python人工智能技术
1. 事务
innodb引擎中支持事务,myisam不支持。
CREATETABLE `users` (
`id` int(11) NOTNULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
`name` varchar(32) DEFAULTNULL,
`amount` int(11) DEFAULTNULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
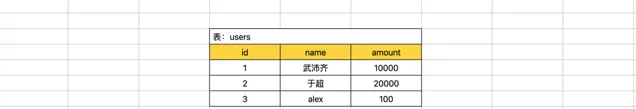
例如:李杰 给 武沛齐 转账 100,那就会涉及2个步骤。
李杰账户 减100
武沛齐账户 加 100
这两个步骤必须同时完成才算完成,并且如果第一个完成、第二步失败,还是回滚到初始状态。
事务,就是来解决这种情况的。 大白话:要成功都成功;要失败都失败。
事务的具有四大特性(ACID):
原子性(Atomicity)
原子性是指事务包含的所有操作不可分割,要么全部成功,要么全部失败回滚。
一致性(Consistency)
执行的前后数据的完整性保持一致。
隔离性(Isolation)
一个事务执行的过程中,不应该受到其他事务的干扰。
持久性(Durability)
事务一旦结束,数据就持久到数据库
1.1 MySQL客户端
mysql>select*from users;
+----+---------+---------+
| id | name | amount |
+----+---------+---------+
|1| wupeiqi |5|
|2| alex |6|
+----+---------+---------+
3rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>begin; -- 开启事务 start transaction;
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>update users set amount=amount-2where id=1; -- 执行操作
Query OK, 1row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql>update users set amount=amount+2where id=2; -- 执行操作
Query OK, 1row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql>commit; -- 提交事务 rollback;
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from users;
+----+---------+---------+
| id | name | amount |
+----+---------+---------+
|1| wupeiqi |3|
|2| ale x |8|
+----+---------+---------+
3rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from users;
+----+---------+---------+
| id | name | amount |
+----+---------+---------+
|1| wupeiqi |3|
|2| ale x |8|
+----+---------+---------+
3rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>begin; -- 开启事务
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>update users set amount=amount-2where id=1; -- 执行操作(此时数据库中的值已修改)
Query OK, 1row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql>rollback; -- 事务回滚(回到原来的状态)
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from users;
+----+---------+---------+
| id | name | amount |
+----+---------+---------+
|1| wupeiqi |3|
|2| ale x |8|
+----+---------+---------+
3rowsinset (0.00 sec)
1.2 Python代码
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8", db='userdb')
cursor= conn.cursor()
# 开启事务
conn.begin()
try:
cursor.execute("update users set amount=1 where id=1")
int('asdf')
cursor.execute("update tran set amount=2 where id=2")
except Exception as e:
# 回滚
print("回滚")
conn.rollback()
else:
# 提交
print("提交")
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
2. 锁
在用MySQL时,不知你是否会疑问:同时有很多做更新、插入、删除动作,MySQL如何保证数据不出错呢?
MySQL中自带了锁的功能,可以帮助我们实现开发过程中遇到的同时处理数据的情况。对于数据库中的锁,从锁的范围来讲有:
表级锁,即A操作表时,其他人对整个表都不能操作,等待A操作完之后,才能继续。
行级锁,即A操作表时,其他人对指定的行数据不能操作,其他行可以操作,等待A操作完之后,才能继续。
MYISAM支持表锁,不支持行锁;
InnoDB引擎支持行锁和表锁。
即:在MYISAM下如果要加锁,无论怎么加都会是表锁。
在InnoDB引擎支持下如果是基于索引查询的数据则是行级锁,否则就是表锁。
所以,一般情况下我们会选择使用innodb引擎,并且在 搜索 时也会使用索引(命中索引)。
接下来的操作就基于innodb引擎来操作:
CREATETABLE `L1` (
`id` int(11) NOTNULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULTNULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULTNULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
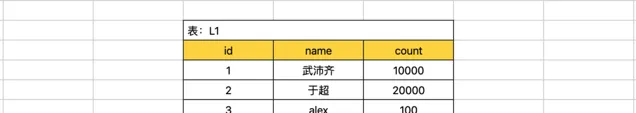
在innodb引擎中,update、insert、delete的行为内部都会先申请锁(排它锁),申请到之后才执行相关操作,最后再释放锁。
所以,当多个人同时像数据库执行:insert、update、delete等操作时,内部加锁后会排队逐一执行。
而select则默认不会申请锁。
select * from xxx;
如果,你想要让select去申请锁,则需要配合 事务 + 特殊语法来实现。
for update
,排它锁,加锁之后,其他不可以读写。
begin;
select*from L1 where name="武沛齐" forupdate; -- name列不是索引(表锁)
commit;
begin; -- 或者 start transaction;
select*from L1 where id=1forupdate; -- id列是索引(行锁)
commit;
lock in share mode
,共享锁,加锁之后,其他可读但不可写。
begin;
select*from L1 where name="武沛齐" lock in share mode; -- 假设name列不是索引(表锁)
commit;
begin; -- 或者 start transaction;
select*from L1 where id=1 lock in share mode; -- id列是索引(行锁)
commit;
2.1 排它锁
排它锁(
for update
),加锁之后,其他事务不可以读写。
应用场景:总共100件商品,每次购买一件需要让商品个数减1 。
A: 访问页面查看商品剩余 100
B: 访问页面查看商品剩余 100
此时 A、B 同时下单,那么他们同时执行SQL:
update goods set count=count-1where id=3
由于Innodb引擎内部会加锁,所以他们两个即使同一时刻执行,内部也会排序逐步执行。
但是,当商品剩余 1个时,就需要注意了。
A: 访问页面查看商品剩余 1
B: 访问页面查看商品剩余 1
此时 A、B 同时下单,那么他们同时执行SQL:
update goods set count=count-1where id=3
这样剩余数量就会出现 -1,很显然这是不正确的,所以应该怎么办呢?
这种情况下,可以利用 排它锁,在更新之前先查询剩余数量,只有数量 >0 才可以购买,所以,下单时应该执行:
begin; -- start transaction;
select count from goods where id=3forupdate;
-- 获取个数进行判断
if 个数>0:
update goods set count=count-1where id=3;
else:
-- 已售罄
commit;
基于Python代码示例:
import pymysql
import threading
deftask():
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8", db='userdb')
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# cursor = conn.cursor()
# 开启事务
conn.begin()
cursor.execute("select id,age from tran where id=2 for update")
# fetchall ( {"id":1,"age":10},{"id":2,"age":10}, ) ((1,10),(2,10))
# {"id":1,"age":10} (1,10)
result = cursor.fetchone()
current_age = result['age']
if current_age > 0:
cursor.execute("update tran set age=age-1 where id=2")
else:
print("已售罄")
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
defrun():
for i inrange(5):
t = threading.Thread(target=task)
t.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
2.2 共享锁
共享锁(
lock in share mode
),可以读,但不允许写。
加锁之后,后续其他事物可以可以进行读,但不允许写(update、delete、insert),因为写的默认也会加锁。
Locking Read Examples
Suppose that you want to insert a new row into a table
child
, and make sure that the child row has a parent row in table
parent
. Your application code can ensure referential integrity throughout this sequence of operations.
First, use a consistent read to query the table
PARENT
and verify that the parent row exists. Can you safely insert the child row to table
CHILD
? No, because some other session could delete the parent row in the moment between your
SELECT
and your
INSERT
, without you being aware of it.
To avoid this potential issue, perform the
SELECT
using
LOCK IN SHARE MODE
:
SELECT*FROM parent WHERE NAME ='Jones' LOCK IN SHARE MODE;
After the
LOCK IN SHARE MODE
query returns the parent
'Jones'
, you can safely add the child record to the
CHILD
table and commit the transaction. Any transaction that tries to acquire an exclusive lock in the applicable row in the
PARENT
table waits until you are finished, that is, until the data in all tables is in a consistent state.
3. 数据库连接池
在操作数据库时需要使用数据库连接池。
pip3.9install pymysql
pip3.9install dbutils
import threading
import pymysql
from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB
MYSQL_DB_POOL = PooledDB(
creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块
maxconnections=5, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数
mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建
maxcached=3, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制
blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错
setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set date style to ...", "set time zone ..."]
ping=0,
# ping MySQL服务端,检查是否服务可用。
# 如:0 = None = never, 1 = default = whenever it is requested,
# 2 = when a cursor is created, 4 = when a query is executed, 7 = always
host='127.0.0.1',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='root123',
database='userdb',
charset='utf8'
)
deftask():
# 去连接池获取一个连接
conn = MYSQL_DB_POOL.connection()
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute('select sleep(2)')
result = cursor.fetchall()
print(result)
cursor.close()
# 将连接交换给连接池
conn.close()
defrun():
for i inrange(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=task)
t.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
4. SQL工具类
基于数据库连接池开发一个公共的SQL操作类,方便以后操作数据库。
4.1 单例和方法
# db.py
import pymysql
from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB
classDBHelper(object):
def__init__(self):
# TODO 此处配置,可以去配置文件中读取。
self.pool = PooledDB(
creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块
maxconnections=5, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数
mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建
maxcached=3, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制
blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错
setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set date style to ...", "set time zone ..."]
ping=0,
# ping MySQL服务端,检查是否服务可用。# 如:0 = None = never, 1 = default = whenever it is requested, 2 = when a cursor is created, 4 = when a query is executed, 7 = always
host='127.0.0.1',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='root123',
database='userdb',
charset='utf8'
)
defget_conn_cursor(self):
conn = self.pool.connection()
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
return conn, cursor
defclose_conn_cursor(self, *args):
for item in args:
item.close()
defexec(self, sql, **kwargs):
conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
conn.commit()
self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor)
deffetch_one(self, sql, **kwargs):
conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
result = cursor.fetchone()
self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor)
return result
deffetch_all(self, sql, **kwargs):
conn, cursor = self.get_conn_cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
result = cursor.fetchall()
self.close_conn_cursor(conn, cursor)
return result
db = DBHelper()
from db import db
db.exec("insert into d1(name) values(%(name)s)", name="武沛齐666")
ret = db.fetch_one("select * from d1")
print(ret)
ret = db.fetch_one("select * from d1 where id=%(nid)s", nid=3)
print(ret)
ret = db.fetch_all("select * from d1")
print(ret)
ret = db.fetch_all("select * from d1 where id>%(nid)s", nid=2)
print(ret)
4.2 上下文管理
如果你想要让他也支持 with 上下文管理。
with 获取连接:
执行SQL(执行完毕后,自动将连接交还给连接池)
# db_context.py
import threading
import pymysql
from dbutils.pooled_db import PooledDB
POOL = PooledDB(
creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块
maxconnections=5, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数
mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建
maxcached=3, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制
blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错
setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set date style to ...", "set time zone ..."]
ping=0,
host='127.0.0.1',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='root123',
database='userdb',
charset='utf8'
)
classConnect(object):
def__init__(self):
self.conn = conn = POOL.connection()
self.cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
def__enter__(self):
return self
def__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
defexec(self, sql, **kwargs):
self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
self.conn.commit()
deffetch_one(self, sql, **kwargs):
self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
result = self.cursor.fetchone()
return result
deffetch_all(self, sql, **kwargs):
self.cursor.execute(sql, kwargs)
result = self.cursor.fetchall()
return result
from db_context import Connect
with Connect() as obj:
# print(obj.conn)
# print(obj.cursor)
ret = obj.fetch_one("select * from d1")
print(ret)
ret = obj.fetch_one("select * from d1 where id=%(id)s", id=3)
print(ret)
总结
本节内容比较重要,也是开发中经常会使用到的技能。
事务,解决批量操作同时成功或失败的问题。
锁,解决并发处理的问题。
数据库连接池,解决多个人请求连接数据库的问题。
SQL工具类,解决连接数据库代码重复的问题。
navicat工具
为了跟上AI时代我干了一件事儿,我创建了一个知识星球社群:ChartGPT与副业。想带着大家一起探索 ChatGPT和新的AI时代 。
有很多小伙伴搞不定ChatGPT账号,于是我们决定,凡是这三天之内加入ChatPGT的小伙伴,我们直接送一个正常可用的永久ChatGPT独立账户。
不光是增长速度最快,我们的星球品质也绝对经得起考验,短短一个月时间,我们的课程团队发布了 8个专栏、18个副业项目 :
简单说下这个星球能给大家提供什么:
1、不断分享如何使用ChatGPT来完成各种任务,让你更高效地使用ChatGPT,以及副业思考、变现思路、创业案例、落地案例分享。
2、分享ChatGPT的使用方法、最新资讯、商业价值。
3、探讨未来关于ChatGPT的机遇,共同成长。
4、帮助大家解决ChatGPT遇到的问题。
5、 提供一整年的售后服务,一起搞副业
星球福利:
1、加入星球4天后,就送ChatGPT独立账号。
2、邀请你加入ChatGPT会员交流群。
3、赠送一份完整的ChatGPT手册和66个ChatGPT副业赚钱手册。
其它福利还在筹划中... 不过,我给你大家保证,加入星球后,收获的价值会远远大于今天加入的门票费用 !
本星球第一期原价 399 ,目前属于试运营,早鸟价 169 ,每超过50人涨价10元,星球马上要来一波大的涨价,如果你还在犹豫,可能最后就要以 更高价格加入了 。。
早就是优势。建议大家尽早以便宜的价格加入!


欢迎有需要的同学试试,如果本文对您有帮助,也请帮忙点个 赞 + 在看 啦!❤️
在 还有更多优质项目系统学习资源,欢迎分享给其他同学吧!
你还有什
么想要补充的吗?
免责声明:本文内容来源于网络,文章版权归原作者所有,意在传播相关技术知识&行业趋势,供大家学习交流,若涉及作品版权问题,请联系删除或授权事宜。
技术君个人微信
添加技术君个人微信即送一份惊喜大礼包
→ 技术资料共享
→ 技术交流社群

--END--
往日热文:
Python程序员深度学习的「四大名著」:

这四本书着实很不错!我们都知道现在机器学习、深度学习的资料太多了,面对海量资源,往往陷入到「无从下手」的困惑出境。而且并非所有的书籍都是优质资源,浪费大量的时间是得不偿失的。给大家推荐这几本好书并做简单介绍。
获得方式:
1.扫码关注本公众号
2.后台回复关键词:名著
▲长按扫描关注,回复名著即可获取











