前言
大家好,我是林三心,有關於
EventLoop
的知識點,在平時是考的非常多的,其實也跟我們日常的工作時息息相關的,懂得
EventLoop
的執行順序,可以大大幫助我們定位出問題出在哪。其實正常的
EventLoop
順序是很容易分辨的,但是如果
setTimeout + Promise + async/await
聯起手來是非常棘手的。今天我就帶大家
過五關斬六將
,征服他們!!!
註明:本文不涉及Nodejs執行機制
同步 && 異步
什麽是異步,什麽是同步,我不多說,我就透過小故事來講講吧。
同步
:你打電話去書店訂書,老板說我查查,你不掛電話在等待,老板把查到的結果告訴你,這期間你不能做自己的事情
異步
:你打電話去書店訂書,老板說我查查,回頭告訴你,你把電話掛了,先去做自己的事情
JS執行機制
其實不難,JavaScript程式碼執行機制,我就歸結為三句話
1、遇到
同步程式碼
直接執行
2、遇到
異步程式碼
先放一邊,並且將他
回呼函式
存起來,存的地方叫
事件佇列
3、等所有
同步程式碼
都執行完,再從
事件佇列
中把存起來的所有
異步回呼函式
拿出來按順序執行

請看以下例子
console.log(1) // 同步
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2) // 異步
}, 2000);
console.log(3) // 同步
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(4) // 異步
}, 0);
console.log(5) // 同步
輸出 : 13542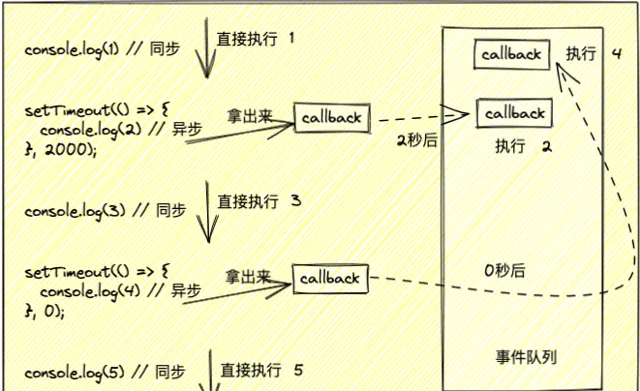
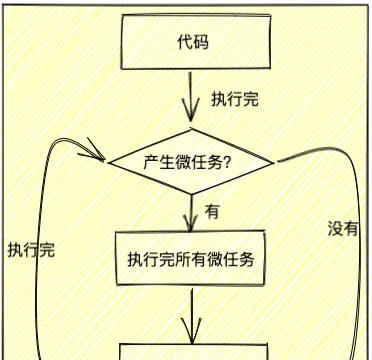
宏任務 && 微任務
前面說了,等所有同步程式碼都執行完,再從
事件佇列
裏依次執行所有
異步回呼函式
。
其實
事件佇列
也是一個小團體,人家也有自己的規則,這就類似於學校管理著許多社團,人家自己社團內部也有人家自己的規矩。
話說回來,為什麽
事件佇列
裏需要有自己的規則呢?要不你先想想為什麽學校裏的社團裏要有自己的規則要分等級,是因為有的人能力強有的人能力弱,所以也就有了等級的高低。其實
事件佇列
也一樣,
事件佇列
是用來存異步回呼的,但是異步也分型別啊,異步任務分為
宏任務
和
微任務
,並且
微任務執行時機先於宏任務
那宏任務和微任務都分別有哪些呢?
宏任務
| # | 瀏覽器 | Node |
|---|---|---|
| I/O | ✅ | ✅ |
| setTimeout | ✅ | ✅ |
| setInterval | ✅ | ✅ |
| setImmediate | ❌ | ✅ |
| requestAnimationFrame | ✅ | ❌ |
微任務
| # | 瀏覽器 | Node |
|---|---|---|
| Promise.prototype.then catch finally | ✅ | ✅ |
| process.nextTick | ❌ | ✅ |
| MutationObserver | ✅ | ❌ |
執行流程
那就來說說整體的執行的流程吧
例子
大家可以根據我的解題步驟去走,基本90%的題目都是沒什麽壓力的!!!
1、標記區分異步和同步
2、異步中,標記區分宏任務和微任務
3、分輪數,一輪一輪慢慢走
console.log(1) // 同步
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2) // 異步:宏任務
});
console.log(3) // 同步
Promise.resolve().then(()=>{ // 異步:微任務
console.log(4)
})
console.log(5) // 同步
第一輪
說明:先把同步的執行輸出
輸出:1,3,5
產生宏任務:
setTimeout
,產生微任務:
Promise.prototype.then
第二輪
說明:微任務先執行
輸出:4
產生宏任務:無,產生微任務:無
剩余宏任務:
setTimeout
,剩余微任務:無
第三輪(結束)
說明:執行宏任務
輸出:2
產生宏任務:無,產生微任務:無
剩余宏任務:無,剩余微任務:無
第一關
想一想我剛剛說的解題思路,大家可以按照那個思路來,這道題也就是分分鐘的事情啦
console.log(1)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(3)
})
});
console.log(4)
newPromise((resolve,reject) => {
console.log(5)
}).then(() => {
console.log(6)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(7)
})
})
console.log(8)
第一步:標記
註意:Promise的
executor
是同步的哦!!!
console.log(1) // 同步
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2) // 異步:宏任務 setTimeout1
Promise.resolve().then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(3)
})
});
console.log(4) // 同步
newPromise((resolve,reject) => {
console.log(5) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(6)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(7) // 異步:宏任務 setTimeout2
})
})
console.log(8) // 同步
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行外層同步輸出 | 1,4,5,8 |
宏任務:
setTimeout1
微任務:
then2
|
宏任務:
setTimeout1
微任務:
then2
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then2
| 6 |
宏任務:
setTimeout2
微任務:無 |
宏任務:
setTimeout1,setTimeout2
微任務:無 |
| 第三輪 |
執行宏任務
setTimeout1
| 2 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1
|
宏任務:
setTimeout2
微任務:
then1
|
| 第四輪 |
執行微任務
then1
| 3 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:
setTimeout2
微任務:無 |
| 第五輪 |
執行宏任務
setTimeout2
| 7 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
第二關
大家在遇到
Promise.then.then
這種時,如果有點懵逼的同學,可以轉換一下,下面會說到
註意:
then
方法會自動返回一個新的
Promise
,也就是
return new Promise
,具體的
Promise源碼
,大家可以看我這篇看了就會,手寫Promise原理,最通俗易懂的版本【閱讀:1.1w,點贊:430】
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(1)
}, 0)
console.log(2)
const p = newPromise((resolve) => {
console.log(3)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(4)
}).then(() => {
console.log(5)
})
console.log(6)
第一步:標記 + 轉換
註意:這裏的轉換,只針對做題時,比較好理解,平時不要這麽轉換,平時這麽轉換是不太合適的,是錯的
setTimeout(() => { // 異步:宏任務 setTimeout
console.log(1)
}, 0)
console.log(2) // 同步
const p = newPromise((resolve) => { // p 是 then1 執行返回的新 Promise
console.log(3) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(4)
// 拿著 p 重新 then
p.then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(5)
})
})
console.log(6) // 同步 6
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行同步輸出 | 2,3,6 |
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:
then1
|
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:
then1
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then1
| 4 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2
|
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:
then2
|
| 第三輪 |
執行微任務
then2
| 5 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:無 |
| 第四輪 |
執行宏任務
setTimeout
| 1 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
第三關
再說一遍:大家在遇到
Promise.then.then
這種時,如果有點懵逼的同學,可以轉換一下
註意:
then
方法會自動返回一個新的
Promise
,也就是
return new Promise
,具體的
Promise源碼
,大家可以看我這篇看了就會,手寫Promise原理,最通俗易懂的版本【閱讀:1.1w,點贊:430】
newPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
console.log(1)
resolve()
}).then(()=>{
console.log(2)
newPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
console.log(3)
resolve()
}).then(()=>{
console.log(4)
}).then(()=>{
console.log(5)
})
}).then(()=>{
console.log(6)
})
第一步:標記 + 轉換
註意:這裏的轉換,只針對做題時,比較好理解,平時不要這麽轉換,平時這麽轉換是不太合適的,是錯的
const p1 = newPromise((resolve, reject) => { // p1 是 then1 執行返回的新 Promise
console.log(1) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(2)
const p2 = newPromise((resolve, reject) => { // p2 是 then2 執行返回的新 Promise
console.log(3) // then1 裏的 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(4)
// 拿著 p2 重新 then
p2.then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then3
console.log(5)
})
})
// 拿著 p1 重新 then
p1.then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then4
console.log(6)
})
})
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行外層同步輸出 | 1 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then1
| 2,3 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then4
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then4
|
| 第三輪 |
執行微任務
then2,then4
| 4,6 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then3
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then3
|
| 第四輪 |
執行微任務
then3
| 5 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
第四關
這一關,比上一關多了一個
return
前面說了,
then
方法會自動返回一個新的
Promise
,相當於
return new Promise
,但是如果你手動寫了
return Promise
,那
return
的就是你手動寫的這個
Promise
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(2)
// 多了個return
returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(3)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(4)
}).then(() => { // 相當於return了這個then的執行返回Promise
console.log(5)
})
}).then(() => {
console.log(6)
})
第一步:標記 + 轉換
由於
return
的是
then3
執行返回的
Promise
,所以
then4
其實是
then3Promise.then()
,所以可轉換為
then3.then4
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(2) // then1 中的 同步
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(3) // then1 中的 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(4)
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then3
console.log(5)
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then4
console.log(6)
})
})
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行外層同步輸出 | 1 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then1
| 2,3 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then3、then4
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then3、then4
|
| 第三輪 |
執行微任務
then2、then3、then4
| 4,5,6 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
第五關
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(1)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(2)
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(3)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(4)
}).then(() => {
console.log(5)
})
}).then(() => {
console.log(6)
})
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(7)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(8)
})
第一步:標記 + 轉換
const p1 = newPromise((resolve, reject) => { // p1 是 then1 執行返回的新 Promise
console.log(1) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(2)
const p2 = newPromise((resolve, reject) => { // p2 是 then2 執行返回的新 Promise
console.log(3) // then1 裏的 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(4)
// 拿著 p2 重新 then
p2.then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then3
console.log(5)
})
})
// 拿著 p1 重新 then
p1.then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then4
console.log(6)
})
})
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(7) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then5
console.log(8)
})
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行外層同步輸出 | 1,7 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1、then5
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then1、then5
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then1、then5
| 2,3,8 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then4
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then2、then4
|
| 第三輪 |
執行微任務
then2、then4
| 4,6 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then5
|
宏任務:無
微任務:
then5
|
| 第四輪 |
執行微任務
then5
| 5 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
第六關
其實
async/await
的內部實作原理,是依賴於
Promise.prototype.then
的不斷巢狀,它在題中也是可以轉換的,下面會講到。
有興趣的朋友可以看我這篇7張圖,20分鐘就能搞定的async/await原理!為什麽要拖那麽久【閱讀量:1.8w,點贊:571】
asyncfunctionasync1() {
console.log(1);
await async2();
console.log(2);
}
asyncfunctionasync2() {
console.log(3);
}
console.log(4);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(5);
});
async1()
newPromise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log(6);
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log(7);
});
console.log(8);
第一步:標記 + 轉換
註意:這裏的轉換,只針對做題時,比較好理解,平時不要這麽轉換,平時這麽轉換是不太合適的
console.log(4); // 同步
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(5); // 異步:宏任務 setTimeout
});
// async1函式可轉換成
console.log(1) // 同步
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(3) // 同步
resolve()
}).then(() => { // 異步:微任務 then1
console.log(2)
})
// async1函式結束
newPromise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log(6); // 同步
resolve();
}).then(function () { // 異步:微任務 then2
console.log(7);
});
console.log(8); // 同步
第二步:分輪
| 輪數 | 說明 | 輸出 | 產生 | 剩余 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一輪 | 執行同步輸出 | 4,1,3,6,8 |
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:
then1、then2
|
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:
then1、then2
|
| 第二輪 |
執行微任務
then1、then2
| 2,7 |
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
宏任務:
setTimeout
微任務:無 |
| 第三輪 |
執行宏任務
setTimeout
| 5 |
宏任務:無
微任務:
then5
|
宏任務:無
微任務:無 |
課後作業
最後給大家布置兩道作業,幫大家鞏固一下本文章所學的知識,大家也可以加入我的摸魚群,進行
答案
的討論。進群點選這裏進群,目前已有將近
1000人
加入學習,我會定時舉辦
學習分享,模擬面試
等學習活動,一起學習,共同進步!!!
第一題(思考題)
想一想下面這兩個有什麽區別?
// 第一種
const p = newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve()
}).then(() =>console.log(1)).then(() =>console.log(2))
// 第二種
const p = newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve()
})
p.then(() =>console.log(1))
p.then(() =>console.log(2))
第二題(問題不大)
asyncfunctionasync1() {
console.log(1);
await async2();
console.log(2);
}
asyncfunctionasync2() {
console.log(3);
}
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
console.log(4)
}, 1000);
}).then(() => {
console.log(5)
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
async1()
resolve()
console.log(6)
}, 1000)
}).then(() => {
console.log(7)
}).then(() => {
console.log(8)
})
}).then(() => {
console.log(9)
})
newPromise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(10)
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
console.log(11)
}, 3000);
}).then(() => {
console.log(12)
})
第三題(有點難度)
這道題能
一分鐘內
做出來的找我領獎,這道題需要具備一定的
Promise原理基礎 + async/await原理基礎
才能比較輕松的答對,有興趣的同學可以看我之前寫過的文章
看了就會,手寫Promise原理,最通俗易懂的版本【閱讀:1.1w,點贊:430】
7張圖,20分鐘就能搞定的async/await原理!為什麽要拖那麽久【閱讀量:1.8w,點贊:571】
asyncfunctionasync1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
asyncfunctionasync2() {
console.log('async start')
returnnewPromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve()
console.log('async2 promise')
})
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0);
async1()
newPromise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise3')
})
console.log('script end')
結語
加入我的摸魚群 ,我會定時直播模擬面試,答疑解惑,先已有將近1000人加入學習













